레보세티리진
| |

| |
| 체계적 명칭 (IUPAC 명명법) | |
|---|---|
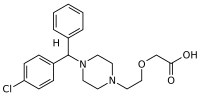
| 2-(2-{4-[(R)-(4-Chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methyl]piperazin-1-yl}ethoxy)acetic acid | |
| 식별 정보 | |
| CAS 등록번호 | 130018-77-8 |
| ATC 코드 | R06AE09 |
| PubChem | 1549000 |
| ChemSpider | 1266001 |
| 화학적 성질 | |
| 화학식 | C21H25ClN2O3 |
| 분자량 | 388.888 g/mol |
| 약동학 정보 | |
| 생체적합성 | High |
| 단백질 결합 | 90% |
| 동등생물의약품 | ? |
| 약물 대사 | 간 14% CYP3A4 |
| 생물학적 반감기 | 6 - 10 시간 |
| 배출 | 신장과 대변 |
| 처방 주의사항 | |
| 임부투여안전성 | B(미국) |
| 법적 상태 | |
| 투여 방법 | 경구 투여 |
레보세티리진(Levocetirizine) 또는 레보세티리진 중염산염(levocetirizine dihydrochloride), 브랜드명 씨잘(Xyzal)은 3세대 비진정성 항히스타민제로, 2세대 세티리진보다 더욱 발전된 형태의 약물이다. 원인이 불분명한 알레르기 비염이나 장기간 일어나는 두드러기 치료에 쓰인다.[1] 구세대 항히스타민제보다는 진정성이 약하다.[2] 구강으로 복용하는 알약 형태이다.[1]
대표적인 부작용으로는 졸음, 입안의 건조감, 기침, 구토, 설사 등이 있다.[1] 임신 중 사용은 안전한 것으로 추정되지만, 연구된 바가 적으며 모유 수유 도중 사용은 안전성이 검토되지 않았다.[3] 레보세티리진은 2세대 항히스타민제처럼 히스타민 H1 수용체를 차단하는 방식으로 작용한다.[4][1]
레보세티리진은 2007년 미국에서 의료용 사용 허가를 받았다.[1] 대한민국에서는 2006년 식품의약품안전처에서 허가를 받았다.[5]
이용[편집]
레보세티리진은 알러지성 비염 증상을 경감시키는 데 사용된다.[6] 알러지성 비염으로 인한 눈물, 콧물, 재채기, 두드러기, 가려움증 등 전형적인 알러지 증상을 감소시키는 효과가 있다.[7]
부작용[편집]
레보세티리진은 비진정성 항히스타민제로 상당한 양을 섭취해도 뇌에 침투하지 못하고 졸음을 유발하지 않는다. 또한 레보세티리진은 건강한 사람에게서 QT 간격의 연장도 크지 않아 심장의 재분극 과정의 안전은 타 항히스타민제보다는 덜 위험하다.[8][9][10] 하지만 일부 사람들에게 졸림, 두통, 구강건조증, 몽롱함, 시력 문제(주로 시야 흐림), 심계항진, 피로 등의 증상이 나타나는 것이 보고되었다.[11]
화학적 특성[편집]
화학적으로 레보세티리진은 세티리진의 활성 좌선성 광학 이성질체로, 세티리진의 좌선 이성질체(l-enantiomer)라고 부르기도 한다.
연구[편집]
가장 최근의 연구인 2006년 9월에서는 레보세티리진이 어린이 천식 발작을 70% 경감해 주는 것으로 나타났다.[12]
각주[편집]
- ↑ 가 나 다 라 마 “Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride Monograph for Professionals”. 《Drugs.com》 (영어). American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. 2019년 3월 22일에 확인함.
- ↑ 《British national formulary : BNF 76》 76판. Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. 280–281쪽. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ↑ “Levocetirizine Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Warnings”. 《Drugs.com》 (영어). 2019년 3월 3일에 확인함.
- ↑ Wallace DV; Dykewicz MS; Bernstein DI; Blessing-Moore J; Cox L; Khan DA; Lang DM; Nicklas RA; Oppenheimer J; Portnoy JM; Randolph CC; Schuller D; Spector SL; Tilles SA (August 2008). “The diagnosis and management of rhinitis: an updated practice parameter”. 《The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology》 122 (2 Suppl): S1–84. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2008.06.003. PMID 18662584.
- ↑ 대한민국 식품의약품안전처. “씨잘정5밀리그램(레보세티리진염산염)”. 의약품안전나라. 2021년 11월 9일에 확인함.
- ↑ Holgate, Stephen; Powell, Richard; Jenkins, Maureen; Ali, Omar (2005년 6월 13일). “A treatment for allergic rhinitis:a view on the role of levocetirizine”. 《Current Medical Research and Opinion》 (Informa Healthcare) 21 (7): 1099–1106. doi:10.1185/030079905x53298. ISSN 0300-7995. PMID 16004679.
The variable efficacy and durability of response of different antihistamines arise from differing modulatory effects on the H(1)-receptor. Conclusion: These findings support both the short-term and long-term use of levocetirizine in the clinical management of allergic rhinitis. The World Health Organization (WHO) ARIA Guidelines (Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma), recommend using a combination of a non-sedating antihistamine with a decongestant, or glucocorticosteroids for treating allergic rhinitis - with the order and combination of treatment depending on severity and duration of symptoms.
- ↑ “Levocetirizine Oral”. WebMD.
- ↑ Hulhoven R; Rosillon D; Letiexhe M; Meeus MA; Daoust A; Stockis A (November 2007). “Levocetirizine does not prolong the QT/QTc interval in healthy subjects: results from a thorough QT study”. 《European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology》 63 (11): 1011–7. doi:10.1007/s00228-007-0366-5. PMID 17891537.
- ↑ “Cetirizine and loratadine: minimal risk of QT prolongation”. 《Prescrire International》 19 (105): 26–8. February 2010. PMID 20455340.
- ↑ Poluzzi E; Raschi E; Godman B; Koci A; Moretti U; Kalaba M; Wettermark B; Sturkenboom M; De Ponti F (2015). “Pro-arrhythmic potential of oral antihistamines (H1): combining adverse event reports with drug utilization data across Europe”. 《PLOS ONE》 10 (3): e0119551. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1019551P. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0119551. PMC 4364720. PMID 25785934.
- ↑ XOZAL technical specifications booklet.
- ↑ Pasquali, M; Baiardini, I; Rogkakou, A; Riccio, AM; Gamalero, C; Descalzi, D; Folli, C; Passalacqua, G; Canonica, GW (September 2006). “Levocetirizine in persistent allergic rhinitis and asthma: effects on symptoms, quality of life and inflammatory parameters”. 《Clinical & Experimental Allergy》 36 (9): 1161–7. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2222.2006.02548.x. PMID 16961716.
