세포 배양: 두 판 사이의 차이
편집 요약 없음 |
잔글 "Cell culture" 문서를 번역하여 만듦 |
||
| 1번째 줄: | 1번째 줄: | ||
[[파일:Cell_Culture_in_a_tiny_Petri_dish.jpg|오른쪽|섬네일| [[샬레]]에서 세포 배양을 하는 모습]] |
|||
{{출처 필요|날짜=2010-9-17}} |
|||
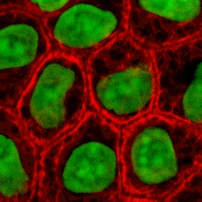
[[파일:Epithelial-cells.jpg|오른쪽|섬네일| [[케라틴]](빨간색)과 [[DNA]](녹색)가 염색된 배양 [[상피 세포]]]] |
|||
{{번역 확장 필요|en|cell culture}} |
|||
'''세포 배양(Cell culture)'''은 일반적으로 자연 환경 외부의 통제된 조건에서 [[세포]]가 성장하는 과정의 총칭이다. 세포는 살아있는 [[조직 (생물학)|조직]]에서 분리된 후에는 신중하게 제어된 조건에서 후속적으로 유지되어야 한다. 이러한 조건은 각 세포 유형에 따라 다르지만 일반적으로 필수 영양소([[아미노산]], [[탄수화물]], [[비타민]], [[광물|무기질]]), 성장인자, [[호르몬]], 가스([[이산화탄소]], [[산소]])를 공급하는 기질 또는 [[배지 (미생물학)|배지]]가 있는 적합한 용기로 구성된다. 이는 물리화학적 환경([[완충 용액]], [[삼투압]], [[온도]])을 조절할 수 있게 설계되었다. 대부분의 세포는 단층(하나의 단일 세포 두께)으로 부착 배양을 형성하기 위해 표면 또는 인공 기질이 필요한 반면, 어떤 세포는 현탁액 배양으로 배지에 자유롭게 떠서 성장할 수 있다.<ref name="Harris">{{저널 인용|제목=Characterizing the mechanics of cultured cell monolayers.|저널=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America|성=Harris|이름=AR|성2=Peter|이름2=L|날짜=9 October 2012|권=109|호=41|쪽=16449–54|doi=10.1073/pnas.1213301109|pmc=3478631|pmid=22991459|성3=Bellis|이름3=J|성4=Baum|이름4=B|성5=Kabla|이름5=AJ|성6=Charras|이름6=GT}}</ref> 대부분의 세포의 수명은 유전적으로 결정되지만 일부 세포 배양 세포는 최적의 조건이 제공되면 무한정 재생되도록 변환되기도 한다. |
|||
'''세포 배양'''(細胞培養, cell culture)은 [[다세포 생물]]에서 [[세포]]를 분리하여, 체외에서 증식시키고 유지하는 일이다. |
|||
실제로 세포 배양이라는 용어는 [[식물 조직 배양]], [[진균 배양]], [[미생물 배양]]의 뜻보다 동물 세포에서 유래된 세포의 배양을 의미한다. 세포 배양의 역사적 발전과 방법은 조직 배양 및 장기 배양 과 밀접한 관련이 있다. [[바이러스]]의 [[숙주]]인 세포와 함께 바이러스 배양도 관련이 있다.<ref name="NIHtimeline">{{웹 인용|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?db=Books&rid=mboc4.table.1516|제목=Some landmarks in the development of tissue and cell culture|확인날짜=2006-04-19}}</ref><ref>{{웹 인용|url=http://www.bioteach.ubc.ca/Bioengineering/CellCulture/index.htm|제목=Cell Culture|확인날짜=2006-04-19}}</ref> |
|||
세포 배양을 할 때 배양 세포는 존재 형태에 따라 접착 배양계 세포와 부유 배양계 세포로 분류할 수 있다. |
|||
== 포유류 세포 배양의 개념 == |
|||
세포 증식이나 기능 실험에서는 다른 요소를 배제하기 위해 무균 조작을 한다. 세포는 생물의 일부이기 때문에 배양 세포의 연구를 통해 생명 현상의 해석을 하기도 하고, 각종 독극물 실험 등에 사용하기도 한다. 또, 세포 배양은 단일 클론 항체 등과 같이 어떤 종류의 물질을 생산하는 수단으로도 이용된다. |
|||
== |
=== 세포의 분리 === |
||
세포는 여러 가지 방법으로 생체 외 배양을 위해 조직에서 분리한다. 세포는 현탁액으로 방출하기 위해 조직을 교반하기 전에 [[콜라겐 분해 효소]], [[트립신]], [[프로네이스]]와 같은 [[효소]]를 사용하여 세포 외 기질을 소화함으로써 고체 조직에서 분리한다.<ref>{{저널 인용|제목=Methods for isolating atrial cells from large mammals and humans|저널=Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology|날짜=September 2015|권=86|쪽=187–98|doi=10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.07.006|pmid=26186893}}</ref><ref>{{저널 인용|제목=Methods in cardiomyocyte isolation, culture, and gene transfer|저널=Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology|날짜=September 2011|권=51|호=3|쪽=288–98|doi=10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.06.012|pmc=3164875|pmid=21723873}}</ref> 또는 조직 조각을 [[배지 (미생물학)|배지]]에 넣고 세포를 배양할 수 있다. |
|||
* 배양 세포 - 체외에서 배양하는 세포다. |
|||
* 초기 배양 - 생물에서 분리하여 세포를 최초로 옮겨 배양하는 것이다. |
|||
* 계대 배양 - 기존의 배양 세포를 새로운 배양 용기로 바꾸어 증식시키고 유지하는 것이다. |
|||
* 배양지 - 세포를 배양하기 위해 사용되는 조직액과 비슷한 성분의 액체다. |
|||
* 간엽계 세포 - 일반적으로 배양이 용이하지만, 표피계 조직의 세포 배양은 상대적으로 어렵다. 또한, 정상세포와 비교하여 암 세포는 비교적 쉽게 배양할 수 있다. |
|||
* 접착 배양계 세포 - 배양 용기에 부착하여 증식하는 배양 세포이며, 계대 시에는 배양지 교환을 실시한다. |
|||
* 부유 배양계 세포 - 배양지 내에서 부유 상태로 증식하는 배양 세포이며, 계대 시에는 배양지 교환을 실시하지 않고 희석 배양을 실시한다. |
|||
* 삼차원 배양 - 특수한 배양법이다. |
|||
* 오염(contamination, 컨테미네이션) - 세포 배양을 목적으로 하는 생물 인자 이외의 생물 인자의 혼입이다. |
|||
** 교차 오염(cross contamination, 크로스 콘테미네이션) - 혼입한 것이 세포인 경우다. |
|||
피험자로부터 직접 배양 된 세포를 1차 세포라고 한다. 일부 종양에서 유래한 것을 제외하고 대부분의 1차 세포는 수명이 제한되어 있다. |
|||
== 같이 보기 == |
|||
{{위키공용분류}} |
|||
* [[P12 세포]] |
|||
[[세포주|불멸 세포주]]는 무작위 돌연변이 또는 [[텔로머레이스]] [[유전자]]의 [[유전자 발현|인공적인 발현]]과 같은 의도적인 변형을 통해 무기한 증식하는 능력을 획득하였다. [[세포 유형|특정 세포 유형]]을 대표하는 수 많은 세포주가 존재한다. |
|||
{{분자생물학}} |
|||
{{전거 통제}} |
|||
=== 배양을 통한 세포 유지 === |
|||
[[분류:생명공학]] |
|||
대부분의 분리된 1차 세포는 [[생물학적 노화]] 과정을 거치고 일반적인 생존 능력(Hayflick 한계)을 유지하면서 특정 인구 수가 되면 [[분열]]을 멈춘다. |
|||
[[분류:세포생물학]] |
|||
[[파일:DMEM_cell_culture_medium.jpg|오른쪽|섬네일| [[DMEM]] 배지]] |
|||
온도 및 가스 혼합물을 제외하고 배양 시스템에서 가장 일반적인 변화 요소는 세포 성장 [[배지 (미생물학)|배지]]이다. 성장 배지의 제조법은 [[수소 이온 농도 지수]], 포도당 농도, 성장 인자 및 기타 영양소의 존재의 여부에 따라 다르다. 배지를 보충하는 데 사용되는 성장 인자는 종종 [[소태아혈청]](FBS), 송아지 혈청, 말혈청, 돼지 혈청과 같은 동물 혈액의 혈청에서 파생된다. 이러한 혈액 유래 성분 성장 인자의 단점은 특히 의료 [[생명공학기술]] 응용 분야에서 [[바이러스]] 또는 [[프리온]]으로 배양물이 오염될 가능성이 있다는 것이다. 현재는 이러한 성분의 사용을 최소화하거나 제거하고 인간 혈소판 용해물(hPL)를 사용함으로 그 단점을 줄일 수 있다.<ref>Hemeda, H., Giebel, B., Wagner, W. (16Feb2014) Evaluation of human platelet lysate versus fetal bovine serum for culture of mesenchymal stromal cells Cytotherapy p170-180 issue 2 doi.10.1016</ref> 이것은 FBS를 인간 세포와 함께 사용할 때 종간 오염에 대한 걱정을 없애준다. hPL은 FBS 또는 기타 동물 혈청을 직접 대체하는 안전하고 신뢰할 수 있는 대안으로 부상했다. 또한, 화학 배지를 사용하여 혈청 흔적(인간 또는 동물)을 제거할 수 있지만 이는 다른 세포 유형에서 항상 달성할 수 있는 것은 아니다. 대체 전략에는 미국, 호주 및 뉴질랜드와 같이 [[소해면상뇌병증|BSE]]/[[전염성해면상뇌병증|TSE]] 위험이 최소인 국가에서 동물 혈액을 조달하고<ref name="bovalco">{{웹 인용|url=http://www.bovalco.com/blog/post/view/9|제목=Post - Blog | Boval BioSolutions, LLC|출판사=bovalco.com|확인날짜=2014-12-02}}</ref> 세포 배양을 위해 전 동물 혈청 대신 혈청에서 추출한 정제된 영양 농축액을 사용하는 것이 포함된다.<ref>{{웹 인용|url=http://www.selbornebiological.com/products/lipimax.htm|제목=LipiMAX purified lipoprotein solution from bovine serum|연도=2006|웹사이트=Selborne Biological Services|보존url=https://www.webcitation.org/68GOR4N9r?url=http://www.selbornebiological.com/products/lipimax.htm|보존날짜=2012-06-08|url-status=dead|확인날짜=2010-02-02}}</ref> |
|||
Plating 밀도(배양 배지 부피 당 세포 수)는 일부 세포 유형에서 중요한 역할을 한다. 예를 들어, Plating 밀도가 낮을수록 과립막 세포는 [[에스트로겐]] 생성을 나타내지만 Plating 밀도가 높으면 [[프로게스테론]]을 생성하는 테카 루테인 세포로 나타난다.<ref>{{저널 인용|제목=Cell plating density alters the ratio of estrogenic to progestagenic enzyme gene expression in cultured granulosa cells|저널=Fertility and Sterility|날짜=April 2010|권=93|호=6|쪽=2050–5|doi=10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.01.151|pmid=19324349}}</ref> |
|||
세포는 현탁액 또는 부착 배양으로 성장할 수 있다.<ref name="Jaccard">{{저널 인용|제목=Automated and online characterization of adherent cell culture growth in a microfabricated bioreactor.|저널=Journal of Laboratory Automation|성=Jaccard|이름=N|성2=Macown|이름2=RJ|날짜=October 2014|권=19|호=5|쪽=437–43|doi=10.1177/2211068214529288|pmc=4230958|pmid=24692228|성3=Super|이름3=A|성4=Griffin|이름4=LD|성5=Veraitch|이름5=FS|성6=Szita|이름6=N}}</ref> 일부 세포는 혈류에 존재하는 세포와 같이 표면에 부착되지 않고 자연적으로 부유 상태로 존재한다. 부착 조건이 허용하는 것보다 더 높은 밀도로 성장할 수 있도록 현탁액 배양에서 생존할 수 있도록 변형된 세포주도 있다. 부착 세포는 부착 특성을 증가시키고 성장 및 분화에 필요한 기타 신호를 제공하기 위해 세포외 기질([[콜라겐]] 및 [[라미닌]]) 성분으로 코팅될 수 있는 조직 배양 플라스틱 또는 미세 담체와 같은 표면이 필요하다. 고형 조직에서 유래한 대부분의 세포는 부착되어 있다. 부착 배양의 또 다른 유형은 2차원 배양 접시와 달리 3차원 환경에서 세포를 성장시키는 것을 포함하는 Organotypic 배양이다'''.''' 이 3D 배양 시스템은 생화학적 및 생리학적으로 생체 내 조직과 더 유사하지만 많은 요인(확산 등)으로 인해 유지 관리하기가 기술적으로 어렵다.<ref>{{저널 인용|제목=Organotypic brain slice cultures: A review|저널=Neuroscience|날짜=October 2015|권=305|쪽=86–98|doi=10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.07.086|pmc=4699268|pmid=26254240}}</ref> |
|||
==== 세포 배양 기초 배지 ==== |
|||
[[생명과학]]에서 일상적으로 사용되는 세포 배양 배지이다. |
|||
* [[최소 필수 배지|MEM]] |
|||
* [[DMEM]] |
|||
* [[RPMI 1640]] |
|||
* [[Ham's F-12]] |
|||
* [[IMDM]] |
|||
* Leibovitz L-15 |
|||
* DMEM/F-12 |
|||
=== 세포 배양 배지의 구성 요소 === |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
!요소 |
|||
! 기능 |
|||
|- |
|||
| 탄소원([[글루코스|포도당]]/[[글루타민]]) |
|||
| 에너지원 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[아미노산]] |
|||
| 단백질 제공 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[비타민]] |
|||
| 세포 생존 및 성장 촉진 |
|||
|- |
|||
| 적절한 농도의 염 |
|||
| 세포 내에서 최적의 [[삼투압]]을 유지하고 효소 반응, [[세포 부착]] 등의 보조 인자로 작용하는 필수 금속 이온을 제공하기 위한 이온의 등장성 혼합물 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[페놀 레드]] 염료 |
|||
| [[산·염기 지시약]]. 페놀 레드의 색상은 pH 7~7.4에서 주황색(혹은 빨간색)에서 산성에서는 노란색으로, 염기성에서는 자주색으로 바뀐다. |
|||
|- |
|||
| 중탄산염/HEPES 완충 용액 |
|||
| 배지에서 균형 잡힌 수소 이온 농도를 유지하는 데 사용된다. |
|||
|} |
|||
==== 전형적인 성장 조건 ==== |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
!조건 |
|||
! |
|||
|- |
|||
| 온도 |
|||
| 37°C |
|||
|- |
|||
| 이산화탄소 |
|||
| 5% |
|||
|- |
|||
| 상대 습도 |
|||
| 95% |
|||
|} |
|||
=== 세포주 교차 오염 === |
|||
세포주 교차 오염은 배양된 세포를 다루는 과학자에게 문제가 될 수 있다.<ref name="Neimark">{{저널 인용|제목=Line of attack|저널=Science|날짜=February 2015|권=347|호=6225|쪽=938–40|bibcode=2015Sci...347..938N|doi=10.1126/science.347.6225.938|pmid=25722392}}</ref> 연구에 따르면 15~20%의 시간에서 실험에 사용된 세포가 잘못 식별되었거나 다른 세포주로 오염된 것으로 나타났다.<ref>{{저널 인용|제목=False human hematopoietic cell lines: cross-contaminations and misinterpretations|저널=Leukemia|날짜=October 1999|권=13|호=10|쪽=1601–7|doi=10.1038/sj.leu.2401510|pmid=10516762}}</ref><ref>{{저널 인용|제목=Cross-contamination: HS-Sultan is not a myeloma but a Burkitt lymphoma cell line|저널=Blood|날짜=December 2001|권=98|호=12|쪽=3495–6|doi=10.1182/blood.V98.12.3495|pmid=11732505}}</ref><ref>{{저널 인용|제목=Identity tests: determination of cell line cross-contamination|저널=Cytotechnology|날짜=June 2006|권=51|호=2|쪽=45–50|doi=10.1007/s10616-006-9013-8|pmc=3449683|pmid=19002894}}</ref> 세포주 교차 오염 문제는 약물 스크리닝 연구에 일상적으로 사용되는 [[NCI-60]]의 세포주에서도 감지되었다.<ref name="chatterjee">{{저널 인용|제목=Cell biology. Cases of mistaken identity|저널=Science|날짜=February 2007|권=315|호=5814|쪽=928–31|doi=10.1126/science.315.5814.928|pmid=17303729}}</ref><ref>{{저널 인용|제목=A case study in misidentification of cancer cell lines: MCF-7/AdrR cells (re-designated NCI/ADR-RES) are derived from OVCAR-8 human ovarian carcinoma cells|저널=Cancer Letters|날짜=January 2007|권=245|호=1–2|쪽=350–2|doi=10.1016/j.canlet.2006.01.013|pmid=16504380}}</ref> [[ATCC]](American Type Culture Collection), [[ECACC]](European Collection of Cell Cultures), [[DSMZ]](German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures)를 포함한 주요 세포주 저장소는 연구자로부터 잘못 식별된 세포주 제출을 받았다.<ref name="chatterjee" /><ref name="macleod">{{저널 인용|제목=Widespread intraspecies cross-contamination of human tumor cell lines arising at source|저널=International Journal of Cancer|날짜=November 1999|권=83|호=4|쪽=555–63|doi=10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19991112)83:4<555::AID-IJC19>3.0.CO;2-2|pmid=10508494}}</ref> 이러한 오염은 세포 배양주를 사용하여 생산된 연구의 품질에 문제를 제기할 수 있다.<ref>{{저널 인용|제목=HeLa cells 50 years on: the good, the bad and the ugly|저널=Nature Reviews. Cancer|날짜=April 2002|권=2|호=4|쪽=315–9|doi=10.1038/nrc775|pmid=12001993}}</ref> ATCC는 [[짧은 탠덤 반복]]( Short Tandem Repeat, STR), [[DNA 지문분석|DNA 지문]]을 사용하여 오염되지 않은 세포주로 인증한다.<ref name="dunham">{{저널 인용|제목=Doing good science: Authenticating cell line identity|저널=Cell Notes|성=Dunham|이름=J.H.|성2=Guthmiller|이름2=P.|url=http://www.promega.com/cnotes/cn022/cn022_15.pdf|연도=2008|권=22|쪽=15–17|보존url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081028200822/http://www.promega.com/cnotes/cn022/cn022_15.pdf|보존날짜=2008-10-28|url-status=dead|확인날짜=2008-10-28}}</ref> |
|||
세포주 교차 오염 문제를 해결하기 위해 연구자들은 세포주의 정체성을 확립하기 위해 초기 계대에서 세포주를 인증하는 것이 좋다. 세포주를 동결하기 전, 활성 배양 동안 2개월마다, 그리고 세포주를 사용하여 생성된 연구 데이터를 출판하기 전에 인증을 반복해야 한다. [[아이소자임|동질효소]] 분석, 인간 림프구 항원(HLA) 유형, 염색체 분석, 핵형 분석, 형태학 및 STR 분석을 비롯한 많은 방법이 세포주를 식별하는 데 사용된다.<ref name="dunham">{{저널 인용|제목=Doing good science: Authenticating cell line identity|저널=Cell Notes|성=Dunham|이름=J.H.|성2=Guthmiller|이름2=P.|url=http://www.promega.com/cnotes/cn022/cn022_15.pdf|연도=2008|권=22|쪽=15–17|보존url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081028200822/http://www.promega.com/cnotes/cn022/cn022_15.pdf|보존날짜=2008-10-28|url-status=dead|확인날짜=2008-10-28}}</ref> |
|||
중요한 세포주 교차 오염의 예중 하나는 [[헬라 세포|헬라 세포주]]이다. |
|||
=== 기타 기술적 문제 === |
|||
세포는 일반적으로 배양에서 계속 분열하기 때문에 일반적으로 사용 가능한 영역 또는 부피를 채우기 위해 성장한다. 이로 인해 몇 가지 문제가 발생할 수 있다. |
|||
* 성장 배지의 영양 고갈 |
|||
* 성장 배지의 pH 변화 |
|||
* [[세포자살|세포 자살]]/[[괴사]] 세포의 축적 |
|||
* 세포 간 접촉은 세포 주기 정지를 자극하여 세포가 분열을 멈추게 하는 접촉 억제 |
|||
* 세포 간 접촉에 따른 [[세포 분화]] |
|||
* 유전적 및 후성적 변화, 변형된 세포의 자연 선택으로 잠재적으로 분화가 감소하고 증식 능력이 증가된 비정상적 배양 적응 세포의 과성장<ref>{{저널 인용|제목=Genetic and epigenetic instability in human pluripotent stem cells|저널=Human Reproduction Update|연도=2012|권=19|호=2|쪽=187–205|doi=10.1093/humupd/dms048|pmid=23223511}}</ref> |
|||
[[배지 (미생물학)|배지]]의 선택은 영양 성분과 농도의 차이로 인해 세포 배양 실험 결과의 생리학적 관련성에 영향을 미칠 수 있다.<ref name="MindYourMedia">{{저널 인용|제목=Mind your media|저널=Nature Metabolism|성=Lagziel S, GottliebE, Shlomi T|url=https://rdcu.be/b8pql|연도=2020|권=2|호=12|쪽=1369–1372|doi=10.1038/s42255-020-00299-y|pmid=33046912}} </ref><ref name="pmid31039782">{{저널 인용|제목=Inferring cancer dependencies on metabolic genes from large-scale genetic screens.|저널=BMC Biol|성=Lagziel S, Lee WD, Shlomi T|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=31039782 |연도=2019|권=17|호=1|쪽=37|doi=10.1186/s12915-019-0654-4|pmc=6489231|pmid=31039782}} </ref> 영양소의 생리학적 수준을 더 잘 나타내는 [[배지 (미생물학)|배지]]를 사용하면 [[생체외|생체 외]] 연구의 생리적 관련성을 향상 시킬 수 있으며 최근에는 Plasmax<ref name="pmid30613774">{{저널 인용|제목=Improving the metabolic fidelity of cancer models with a physiological cell culture medium.|저널=Sci Adv|성=Vande Voorde J, Ackermann T, Pfetzer N, Sumpton D, Mackay G, Kalna G|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=30613774 |연도=2019|권=5|호=1|쪽=eaau7314|bibcode=2019SciA....5.7314V|doi=10.1126/sciadv.aau7314|pmc=6314821|pmid=30613774|저자표시=etal}} </ref> 및 Human Plasma Like Medium(HPLM)<ref name="pmid28388410">{{저널 인용|제목=Physiologic Medium Rewires Cellular Metabolism and Reveals Uric Acid as an Endogenous Inhibitor of UMP Synthase.|저널=Cell|성=Cantor JR, Abu-Remaileh M, Kanarek N, Freinkman E, Gao X, Louissaint A|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=28388410 |연도=2017|권=169|호=2|쪽=258–272.e17|doi=10.1016/j.cell.2017.03.023|pmc=5421364|pmid=28388410|저자표시=etal}}</ref> 과 같은 배지 유형이 개발되었다. |
|||
=== 배양 세포의 조작 === |
|||
배양 세포에서 수행되는 일반적인 조작 중에는 배지 변경, 세포 계대, 세포 [[형질 주입]]이 있다. 이들은 일반적으로 무균 기술에 의존하는 조직 배양 방법을 사용하여 수행된다. 무균 기술은 [[세균]], [[효모]] 또는 기타 세포주의 오염을 방지하는 것을 목표로 한다. 조작은 일반적으로 오염 미생물을 배제하기 위해 [[생물 안전 작업대]] 또는 [[층류 작업대]]에서 수행된다. [[항생물질|항생제]]([[페니실린]], [[스트렙토마이신]]) 및 [[항진균제]]([[암포테리신 B]])도 배지에 첨가할 수 있다. |
|||
세포가 대사 과정을 거치면서 산이 생성되고 pH가 감소한다. [[산·염기 지시약]]을 배지에 첨가하여 영양소 고갈을 측정한다. |
|||
부착 배양의 경우 흡인에 의해 배지를 직접 제거한 다음 교체할 수 있다. |
|||
==== 세포의 Passage ==== |
|||
[[계대 배양]]에는 소수의 세포를 새 용기로 옮기는 작업이 포함된다. 세포를 규칙적으로 분할하면 장기간 높은 세포 밀도와 관련된 노화를 방지하므로 세포를 더 오랜 시간 동안 배양할 수 있다. 현탁 배양은 더 많은 양의 신선한 배지에 희석된 몇 개의 세포를 포함하는 소량의 배양으로 쉽게 계대된다. 부착 배양의 경우 먼저 용기에서 세포를 분리해야 한다. [[트립신]]/[[EDTA]]의 혼합물을 이용한다. 그런 다음 소수의 분리된 세포를 사용하여 새로운 용기에 옮겨 담는다. RAW 세포와 같은 일부 세포 배양은 고무 Scraper로 용기 표면에서 물리적으로 긁어낸다. |
|||
==== 형질 전환 및 형질 도입 ==== |
|||
세포를 조작하는 또 다른 일반적인 방법은 [[형질주입|형질 주입]]에 의한 외래 DNA의 도입을 포함한다. 이것은 세포가 관심 유전자를 발현하도록 하기 위해 수행된다. 최근에 [[RNA 간섭]] 구조의 형질 주입은 특정 유전자 및 단백질의 발현을 억제하기 위한 편리한 메커니즘으로 실현되었다. 또한 DNA는 [[형질 도입]] 또는 [[형질전환|형질 전환]]이라고 하는 방법으로 바이러스를 사용하여 세포에 삽입될 수 있다. 바이러스는 기생체이기 때문에 정상적인 번식 과정의 일부이기 때문에 DNA를 세포에 도입하는 데 매우 적합하다. |
|||
=== 확립된 인간 세포주 === |
|||
== 일반적인 세포주 == |
|||
; 인간 세포주 |
|||
* DU145 ([[전립선암]]) |
|||
* H295R (부신피질암) |
|||
* [[헬라 세포|HeLa]] ( [[자궁경부암]] ) |
|||
* KBM-7 ([[만성 골수성 백혈병]]) |
|||
* LNCaP ([[전립선암]]) |
|||
* MCF-7 ([[유방암]]) |
|||
* MDA-MB-468 ([[유방암]]) |
|||
* PC3 ([[전립선암]]) |
|||
* SaOS-2 ([[골종양]]) |
|||
* SH-SY5Y ([[신경모세포종]], [[다발성 골수종]]) |
|||
* T-47D ([[유방암]]) |
|||
* THP-1 ([[급성 골수성 백혈병]]) |
|||
* U87 ([[교모세포종]]) |
|||
; 영장류 세포주 |
|||
* Vero ([[버빗원숭이속]] 신장 [[상피 조직|상피]] 세포) |
|||
; 쥐 세포주 |
|||
* MC3T3 (배아 [[머리덮개뼈|Calvarium]]) |
|||
; 쥐 종양 세포주 |
|||
* GH3 ([[뇌하수체 샘종]]) |
|||
* [[P12 세포|PC12]] ([[크롬친화세포종]]) |
|||
; 식물 세포주 |
|||
* [[담배 BY-2]] (세포 현탁 배양으로 보관, 식물 세포의 [[모델 생물]]) |
|||
; 기타 종 세포주 |
|||
* MDCK ([[개]] 신장 [[상피 조직|상피]]) |
|||
* A6 (Xenopus 신장 상피) |
|||
* AB9 ([[제브라피쉬]]) |
|||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="width:100%;" |
|||
!Cell line |
|||
!Meaning |
|||
!Organism |
|||
!Origin tissue |
|||
![[형태학 (생물학)|Morphology]] |
|||
!Links |
|||
|- |
|||
|3T3-L1 |
|||
|"3-day transfer, inoculum 3 x 10^5 cells" |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Embryo |
|||
|Fibroblast |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=86052701&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0123 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|4T1 |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Mammary gland |
|||
| |
|||
|[http://www.atcc.org/products/all/CRL-2539.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0125 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|1321N1 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Brain |
|||
|Astrocytoma |
|||
|[https://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=86030402&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0110 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|9L |
|||
| |
|||
|Rat |
|||
|Brain |
|||
|Glioblastoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=94110705&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_1928 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|A172 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Brain |
|||
|Glioblastoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=88062428&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0131 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|A20 |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|B [[림프종|lymphoma]] |
|||
|B [[림프구|lymphocyte]] |
|||
|[https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_1940 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|A253 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Submandibular duct |
|||
|Head and neck carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.atcc.org/products/all/HTB-41.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_1060 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|A2780 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Ovary |
|||
|Ovarian carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=93112519&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0134 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|A2780ADR |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Ovary |
|||
|Adriamycin-resistant derivative of A2780 |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=93112520&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_1941 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|A2780cis |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Ovary |
|||
|Cisplatin-resistant derivative of A2780 |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=93112517&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_1942 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|A431 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Skin epithelium |
|||
|Squamous cell carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=85090402&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0037 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|A549 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lung |
|||
|Lung carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=86012804&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0023 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|AB9 |
|||
| |
|||
|[[제브라피쉬|Zebrafish]] |
|||
|Fin |
|||
|Fibroblast |
|||
|[http://www.atcc.org/products/all/CRL-2298.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_6311 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|AHL-1 |
|||
|Armenian Hamster Lung-1 |
|||
|Hamster |
|||
|Lung |
|||
| |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=90120504&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_4611 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|ALC |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Bone marrow |
|||
|Stroma |
|||
|{{PMID|2435412}}<ref name="Missingor">{{저널 인용|제목=A single bone marrow-derived stromal cell type supports the in vitro growth of early lymphoid and myeloid cells|저널=Cell|날짜=March 1987|권=48|호=6|쪽=997–1007|doi=10.1016/0092-8674(87)90708-2|pmid=2435412}}</ref> [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0E84 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|B16 |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|[[흑색종|Melanoma]] |
|||
| |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/search.jsp?searchtext=B16&dosearch=true ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_F936 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|B35 |
|||
| |
|||
|Rat |
|||
|Neuroblastoma |
|||
| |
|||
|[http://www.atcc.org/products/all/CRL-2754.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_1951 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|BCP-1 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|[[말초 혈액 단핵세포|PBMC]] |
|||
|HIV+ primary effusion lymphoma |
|||
|[http://www.atcc.org/products/all/CRL-2294.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0107 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|BEAS-2B |
|||
|Bronchial epithelium + Adenovirus 12-SV40 virus hybrid (Ad12SV40) |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lung |
|||
|Epithelial |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=95102433&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0168 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|bEnd.3 |
|||
|Brain Endothelial 3 |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Brain/[[대뇌 피질|cerebral cortex]] |
|||
|Endothelium |
|||
|[https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0170 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|BHK-21 |
|||
|Baby Hamster Kidney-21 |
|||
|Hamster |
|||
|Kidney |
|||
|[[섬유아세포|Fibroblast]] |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/search.jsp?searchtext=BHK-21&dosearch=true ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_1915 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|BOSC23 |
|||
|Packaging cell line derived from HEK 293 |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Kidney (embryonic) |
|||
|Epithelium |
|||
|[https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_4401 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|BT-20 |
|||
|Breast Tumor-20 |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Breast epithelium |
|||
|Breast carcinoma |
|||
|[https://www.atcc.org/products/all/HTB-19.aspx ATCC] [http://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0178 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|BxPC-3 |
|||
|Biopsy xenograft of Pancreatic Carcinoma line 3 |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Pancreatic adenocarcinoma |
|||
|Epithelial |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=93120816&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0186 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|C2C12 |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Myoblast |
|||
| |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=91031101&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0188 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|C3H-10T1/2 |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Embryonic mesenchymal cell line |
|||
| |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=99072801&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0190 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|C6 |
|||
| |
|||
|Rat |
|||
|Brain [[별 아교 세포|astrocyte]] |
|||
|[[교종 (의학)|Glioma]] |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=92090409&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0194 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|C6/36 |
|||
| |
|||
|Insect - [[흰줄숲모기|Asian tiger mosquito]] |
|||
|Larval tissue |
|||
| |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=89051705&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_Z230 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|Caco-2 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Colon |
|||
|Colorectal carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=86010202&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0025 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|Cal-27 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Tongue |
|||
|Squamous cell carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.atcc.org/products/all/CRL-2095.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_1107 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|Calu-3 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lung |
|||
|Adenocarcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.atcc.org/products/all/HTB-55.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0609 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|CGR8 |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Embryonic stem cells |
|||
| |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=07032901&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_3987 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|CHO |
|||
|Chinese Hamster Ovary |
|||
|Hamster |
|||
|Ovary |
|||
|Epithelium |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/search.jsp?searchtext=CHO&dosearch=true ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cgi-bin/cellosaurus/search?input=CHO Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|CML T1 |
|||
|Chronic myeloid leukemia T lymphocyte 1 |
|||
|Human |
|||
|CML acute phase |
|||
|T cell leukemia |
|||
|[http://www.dsmz.de/catalogues/details/culture/ACC-7.html DSMZ] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_1126 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|CMT12 |
|||
|Canine Mammary Tumor 12 |
|||
|Dog |
|||
|Mammary gland |
|||
|Epithelium |
|||
|[https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_L329 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|COR-L23 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lung |
|||
|Lung carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=92031919&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_1139 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|COR-L23/5010 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lung |
|||
|Lung carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=96042338&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2006 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|COR-L23/CPR |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lung |
|||
|Lung carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=96042336&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2007 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|COR-L23/R23- |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lung |
|||
|Lung carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=96042337&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2009 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|COS-7 |
|||
|''Cercopithecus aethiops'', origin-defective SV-40 |
|||
|Old World monkey - ''Cercopithecus aethiops'' (''[[버빗원숭이속|Chlorocebus]]'') |
|||
|Kidney |
|||
|Fibroblast |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=87021302&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0224 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|COV-434 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Ovary |
|||
|Ovarian granulosa cell carcinoma |
|||
|{{PMID|8436435}}<ref name="Missingor_a">{{저널 인용|제목=Establishment and characterization of 7 ovarian carcinoma cell lines and one granulosa tumor cell line: growth features and cytogenetics|저널=International Journal of Cancer|날짜=February 1993|권=53|호=4|쪽=613–20|doi=10.1002/ijc.2910530415|pmid=8436435|저자표시=6}}</ref> [http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=07071909&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2010 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|CT26 |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Colon |
|||
|Colorectal carcinoma |
|||
|[https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_7254 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|D17 |
|||
| |
|||
|Dog |
|||
|Lung metastasis |
|||
|[[골육종|Osteosarcoma]] |
|||
|[http://www.atcc.org/products/all/CCL-183.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_1916 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|DAOY |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Brain |
|||
|Medulloblastoma |
|||
|[https://www.atcc.org/Products/All/HTB-186.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_1167 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|DH82 |
|||
| |
|||
|Dog |
|||
|Histiocytosis |
|||
|[[단핵구|Monocyte]]/[[대식세포|macrophage]] |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=94062922&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2018 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|DU145 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|[[안드로겐|Androgen]] insensitive prostate carcinoma |
|||
| |
|||
|[http://www.atcc.org/products/all/HTB-81.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0105 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|DuCaP |
|||
|Dura mater cancer of the Prostate |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Metastatic prostate carcinoma |
|||
|Epithelial |
|||
|{{PMID|11317521}}<ref name="Lee2001">{{저널 인용|제목=Establishment and characterization of a new human prostatic cancer cell line: DuCaP|저널=In Vivo|연도=2001|권=15|호=2|쪽=157–62|pmid=11317521}}</ref> [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2025 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|E14Tg2a |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
| |
|||
|Embryonic stem cells |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=08021401&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_9108 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|EL4 |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
| |
|||
|T cell leukemia |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=85023105&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0255 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|EM-2 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|CML blast crisis |
|||
|Ph+ CML line |
|||
|[http://www.dsmz.de/catalogues/details/culture/ACC-135.html DSMZ] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_1196 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|EM-3 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|CML blast crisis |
|||
|Ph+ CML line |
|||
|[http://www.dsmz.de/catalogues/details/culture/ACC-134.html DSMZ] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2033 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|EMT6/AR1 |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Mammary gland |
|||
|Epithelial-like |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=96042327&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_1924 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|EMT6/AR10.0 |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Mammary gland |
|||
|Epithelial-like |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=96042326&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_1925 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|FM3 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lymph node metastasis |
|||
|[[흑색종|Melanoma]] |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=13012407&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2046 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|GL261 |
|||
|Glioma 261 |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Brain |
|||
|Glioma |
|||
|[https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_Y003 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|H1299 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lung |
|||
|Lung carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.atcc.org/products/all/CRL-5803.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0060 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|HaCaT |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Skin |
|||
|Keratinocyte |
|||
|[http://www.clsgmbh.de/p800_HaCaT.html CLS] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0038 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|HCA2 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Colon |
|||
|Adenocarcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=06061901&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2056 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|HEK 293 |
|||
|Human Embryonic Kidney 293 |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Kidney (embryonic) |
|||
|Epithelium |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=85120602&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0045 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|HEK 293T |
|||
|HEK 293 derivative |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Kidney (embryonic) |
|||
|Epithelium |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=12022001&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0063 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[헬라 세포|HeLa]] |
|||
|"Henrietta Lacks" |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Cervix epithelium |
|||
|Cervical carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=93021013&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0030 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|Hepa1c1c7 |
|||
|Clone 7 of clone 1 hepatoma line 1 |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Hepatoma |
|||
|Epithelial |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=95090613&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0328 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|Hep G2 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Liver |
|||
|Hepatoblastoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=85011430&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0027 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|High Five |
|||
| |
|||
|Insect (moth) - ''Trichoplusia ni'' |
|||
|Ovary |
|||
| |
|||
|[https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_C190 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|HL-60 |
|||
|Human Leukemia-60 |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Blood |
|||
|Myeloblast |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=98070106&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0002 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|HT-1080 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
| |
|||
|Fibrosarcoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=85111505&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0317 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|HT-29 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Colon epithelium |
|||
|Adenocarcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=91072201&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0320 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|J558L |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Myeloma |
|||
|B lymphocyte cell |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=88032902&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_3949 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|Jurkat |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|White blood cells |
|||
|T cell [[백혈병|leukemia]] |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=88042803&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0065 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|JY |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lymphoblastoid |
|||
|EBV-transformed B cell |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/hlatyped/detail.jsp?refId=94022533&collection=ecacc_hlad ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0108 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|K562 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lymphoblastoid |
|||
|CML blast crisis |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=89121407&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0004 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|KBM-7 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lymphoblastoid |
|||
|CML blast crisis |
|||
|[https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_A426 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|KCL-22 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lymphoblastoid |
|||
|CML |
|||
|[http://www.dsmz.de/catalogues/details/culture/ACC-519.html DSMZ] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2091 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|KG1 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lymphoblastoid |
|||
|AML |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=86111306&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0374 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|Ku812 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lymphoblastoid |
|||
|Erythroleukemia |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=90071807&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0379 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|KYO-1 |
|||
|Kyoto-1 |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lymphoblastoid |
|||
|CML |
|||
|[http://www.dsmz.de/catalogues/details/culture/ACC-601.html DSMZ] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2095 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|L1210 |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Lymphocytic leukemia |
|||
|Ascitic fluid |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=87092804&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0382 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|L243 |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Hybridoma |
|||
|Secretes L243 mAb (against HLA-DR) |
|||
|[http://www.atcc.org/products/all/HB-55.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_4533 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|LNCaP |
|||
|Lymph Node Cancer of the Prostate |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Prostatic adenocarcinoma |
|||
|Epithelial |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=89110211&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0395 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|MA-104 |
|||
|Microbiological Associates-104 |
|||
|African Green Monkey |
|||
|Kidney |
|||
|Epithelial |
|||
|[https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_3845 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|MA2.1 |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Hybridoma |
|||
|Secretes MA2.1 mAb (against HLA-A2 and HLA-B17) |
|||
|[http://www.atcc.org/products/all/HB-54.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_L672 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|Ma-Mel 1, 2, 3....48 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Skin |
|||
|A range of [[흑색종|melanoma]] cell lines |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/search.jsp?searchtext=Ma-Mel&dosearch=true ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cgi-bin/cellosaurus/search?input=Ma-mel Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|MC-38 |
|||
|Mouse Colon-38 |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Colon |
|||
|Adenocarcinoma |
|||
|[https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_B288 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|MCF-7 |
|||
|Michigan Cancer Foundation-7 |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Breast |
|||
|Invasive breast ductal carcinoma ER+, PR+ |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=86012803&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0031 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|MCF-10A |
|||
|Michigan Cancer Foundation-10A |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Breast epithelium |
|||
| |
|||
|[http://www.atcc.org/products/all/CRL-10317.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0598 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|MDA-MB-157 |
|||
|M.D. Anderson - Metastatic Breast-157 |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Pleural effusion metastasis |
|||
|Breast carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=92020422&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0618 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|MDA-MB-231 |
|||
|M.D. Anderson - Metastatic Breast-231 |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Pleural effusion metastasis |
|||
|Breast carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=92020424&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0062 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|MDA-MB-361 |
|||
|M.D. Anderson - Metastatic Breast-361 |
|||
|Human |
|||
| |
|||
|[[흑색종|Melanoma]] (contaminated by M14) |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=92020423&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0620 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|MDA-MB-468 |
|||
|M.D. Anderson - Metastatic Breast-468 |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Pleural effusion metastasis |
|||
|Breast carcinoma |
|||
|[https://www.atcc.org/products/all/HTB-132.aspx ATCC] [http://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0419 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|MDCK II |
|||
|Madin Darby Canine Kidney II |
|||
|Dog |
|||
|Kidney |
|||
|Epithelium |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=00062107&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0424 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|MG63 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Bone |
|||
|Osteosarcoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=86051601&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0426 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|MIA PaCa-2 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Prostate |
|||
|Pancreatic Carcinoma |
|||
|[https://www.atcc.org/Products/All/CRL-1420.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0428 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|MOR/0.2R |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lung |
|||
|Lung carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=96042335&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2126 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|Mono-Mac-6 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|White blood cells |
|||
|Myeloid metaplasic [[급성 골수성 백혈병|AML]] |
|||
|[https://www.dsmz.de/catalogues/details/culture/ACC-124.html DSMZ] [http://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_1426 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|MRC-5 |
|||
|Medical Research Council cell strain 5 |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lung (fetal) |
|||
|Fibroblast |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=97112601&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0440 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|MTD-1A |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
| |
|||
|Epithelium |
|||
|[https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_EG11 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|MyEnd |
|||
|Myocardial Endothelial |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
| |
|||
|Endothelium |
|||
|[https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2131 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|NCI-H69 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lung |
|||
|Lung carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=91091802&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_1579 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|NCI-H69/CPR |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lung |
|||
|Lung carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=96042328&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2137 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|NCI-H69/LX10 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lung |
|||
|Lung carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=96042331&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2138 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|NCI-H69/LX20 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lung |
|||
|Lung carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=96042332&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2139 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|NCI-H69/LX4 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lung |
|||
|Lung carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=96042329&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2140 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|Neuro-2a |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Nerve/neuroblastoma |
|||
|Neuronal stem cells |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=89121404&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0470 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|NIH-3T3 |
|||
|[[국립보건원 (미국)|NIH]], 3-day transfer, inoculum 3 x 10<sup>5</sup> cells |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Embryo |
|||
|Fibroblast |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=93061524&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0594 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|NALM-1 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Peripheral blood |
|||
|Blast-crisis CML |
|||
|[http://www.atcc.org/products/all/CRL-1567.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0091 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|NK-92 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Leukemia/lymphoma |
|||
| |
|||
|[http://www.atcc.org/products/all/CRL-2407.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2142 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|NTERA-2 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lung metastasis |
|||
|Embryonal carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=01071221&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_3407 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|NW-145 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Skin |
|||
|[[흑색종|Melanoma]] |
|||
|[http://www.ebi.ac.uk/cgi-bin/ipd/estdab/print_cell.cgi?ESTDAB-057 ESTDAB] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2148 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|OK |
|||
|Opossum Kidney |
|||
|[[버지니아주머니쥐|Virginia opossum]] - ''Didelphis virginiana'' |
|||
|Kidney |
|||
| |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=91021202&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0472 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|OPCN / OPCT cell lines |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Prostate |
|||
|Range of prostate tumour lines |
|||
|[https://web.expasy.org/cgi-bin/cellosaurus/search?input=CLPUB00242 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|P3X63Ag8 |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Myeloma |
|||
| |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=85011401&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_3411 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|PANC-1 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Duct |
|||
|Epithelioid Carcinoma |
|||
|[https://www.atcc.org/Products/All/CRL-1469.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0480 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[P12 세포|PC12]] |
|||
| |
|||
|Rat |
|||
|[[부신속질|Adrenal medulla]] |
|||
|[[크롬친화세포종|Pheochromocytoma]] |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=88022401&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0481 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|PC-3 |
|||
|Prostate Cancer-3 |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Bone metastasis |
|||
|Prostate carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=90112714&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0035 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|Peer |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|T cell leukemia |
|||
| |
|||
|[http://www.dsmz.de/catalogues/details/culture/ACC-6.html DSMZ] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_1913 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|PNT1A |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|[[전립샘|Prostate]] |
|||
|SV40-transformed tumour line |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=95012614&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2163 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|PNT2 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|[[전립샘|Prostate]] |
|||
|SV40-transformed tumour line |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=95012613&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2164 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|Pt K2 |
|||
|The second cell line derived from ''Potorous tridactylis'' |
|||
|[[긴코쥐캥거루|Long-nosed potoroo]] - ''Potorous tridactylus'' |
|||
|Kidney |
|||
|Epithelial |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=88031601&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0514 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|Raji |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|B [[림프종|lymphoma]] |
|||
|Lymphoblast-like |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=85011429&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0511 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|RBL-1 |
|||
|Rat Basophilic Leukemia-1 |
|||
|Rat |
|||
|Leukemia |
|||
|Basophil cell |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=86061001&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0496 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|RenCa |
|||
|Renal Carcinoma |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Kidney |
|||
|Renal carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.atcc.org/products/all/CRL-2947.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2174 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|RIN-5F |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Pancreas |
|||
| |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=95090402&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2177 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|RMA-S |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
| |
|||
|T cell tumour |
|||
|[https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2180 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|S2 |
|||
|Schneider 2 |
|||
|Insect - ''[[노랑초파리|Drosophila melanogaster]]'' |
|||
|Late stage (20–24 hours old) embryos |
|||
| |
|||
|[https://www.atcc.org/products/all/CRL-1963.aspx ATCC] [http://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_Z232 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|SaOS-2 |
|||
|Sarcoma OSteogenic-2 |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Bone |
|||
|Osteosarcoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=89050205&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0548 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|Sf21 |
|||
|''Spodoptera frugiperda'' 21 |
|||
|Insect (moth) - ''[[열대거세미나방|Spodoptera frugiperda]]'' |
|||
|Ovary |
|||
| |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=05022801&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0518 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|Sf9 |
|||
|''Spodoptera frugiperda'' 9 |
|||
|Insect (moth) - ''[[열대거세미나방|Spodoptera frugiperda]]'' |
|||
|Ovary |
|||
| |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=89070101&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0549 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|SH-SY5Y |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Bone marrow metastasis |
|||
|Neuroblastoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=94030304&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0019 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|SiHa |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Cervix epithelium |
|||
|Cervical carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.atcc.org/products/all/HTB-35.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0032 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|SK-BR-3 |
|||
|Sloan-Kettering Breast cancer 3 |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Breast |
|||
|Breast carcinoma |
|||
|[https://www.dsmz.de/catalogues/details/culture/ACC-736.html DSMZ] [http://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0033 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|SK-OV-3 |
|||
|Sloan-Kettering Ovarian cancer 3 |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Ovary |
|||
|Ovarian carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=91091004&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0532 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|SK-N-SH |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Brain |
|||
|Epithelial |
|||
|[https://www.atcc.org/Products/All/HTB-11.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0531 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|T2 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
| |
|||
|T cell leukemia/B cell line hybridoma |
|||
|[http://www.atcc.org/products/all/CRL-1992.aspx ATCC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2211 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|T-47D |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Breast |
|||
|Breast ductal carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=85102201&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0553 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|T84 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lung metastasis |
|||
|Colorectal carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=88021101&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0555 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|T98G |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Glioblastoma-astrocytoma |
|||
|Epithelium |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=92090213&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0556 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|THP-1 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Monocyte |
|||
|Acute monocytic leukemia |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=88081201&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0006 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|U2OS |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Osteosarcoma |
|||
|Epithelial |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=92022711&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0042 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|U373 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Glioblastoma-astrocytoma |
|||
|Epithelium |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/search.jsp?searchtext=U373%20&dosearch=true ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2219 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|U87 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Glioblastoma-astrocytoma |
|||
|Epithelial-like |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=89081402&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0022 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|U937 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Leukemic monocytic lymphoma |
|||
| |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=85011440&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0007 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|VCaP |
|||
|Vertebral Cancer of the Prostate |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Vertebra metastasis |
|||
|Prostate carcinoma |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=06020201&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2235 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|Vero |
|||
|From Esperanto: ''verda'' (green, for green monkey) ''reno'' (kidney) |
|||
|African green monkey - ''Chlorocebus sabaeus'' |
|||
|Kidney epithelium |
|||
| |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=84113001&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0059 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|VG-1 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
| |
|||
|Primary effusion lymphoma |
|||
|[https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_0106 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|WM39 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Skin |
|||
|[[흑색종|Melanoma]] |
|||
|[http://www.ebi.ac.uk/cgi-bin/ipd/estdab/print_cell.cgi?ESTDAB-080 ESTDAB] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2240 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|WT-49 |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lymphoblastoid |
|||
| |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/hlatyped/detail.jsp?refId=86052108&collection=ecacc_hlad ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2242 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|YAC-1 |
|||
| |
|||
|Mouse |
|||
|Lymphoma |
|||
| |
|||
|[http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/generalcell/detail.jsp?refId=86022801&collection=ecacc_gc ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2244 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|- |
|||
|YAR |
|||
| |
|||
|Human |
|||
|Lymphoblastoid |
|||
|EBV-transformed B cell |
|||
|[https://web.archive.org/web/20080920120901/http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6T3B-3VWP1CN-2&_user=2471587&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&view=c&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=2471587&md5=93582a8dcb31e96760f4b9a618936c92 Human Immunology]<ref>{{저널 인용|제목=Promiscuous T-cell recognition of a rubella capsid protein epitope restricted by DRB1*0403 and DRB1*0901 molecules sharing an HLA DR supertype|저널=Human Immunology|날짜=March 1998|권=59|호=3|쪽=149–57|doi=10.1016/S0198-8859(98)00006-8|pmid=9548074}}</ref> [http://www.phe-culturecollections.org.uk/products/celllines/hlatyped/detail.jsp?refId=95042721&collection=ecacc_hlad ECACC] [https://web.expasy.org/cellosaurus/CVCL_2192 Cellosaurus] |
|||
|} |
|||
== 참고 == |
|||
* [[생물학에서의 영생]] |
|||
* 세포 배양 분석 |
|||
* 전기적 세포-기질 임피던스 감지 |
|||
* 오염된 세포주 목록 |
|||
* NCI-60 세포주의 목록 |
|||
* 유방암 세포주 목록 |
|||
* 미세생리계 |
|||
[[분류:분자생물학 기술]] |
[[분류:분자생물학 기술]] |
||
[[분류:세포생물학]] |
|||
[[분류:생명공학]] |
|||
[[분류:세포 배양]] |
|||
[[분류:번역이 검토되지 않은 문서]] |
|||
2021년 11월 24일 (수) 15:05 판

세포 배양(Cell culture)은 일반적으로 자연 환경 외부의 통제된 조건에서 세포가 성장하는 과정의 총칭이다. 세포는 살아있는 조직에서 분리된 후에는 신중하게 제어된 조건에서 후속적으로 유지되어야 한다. 이러한 조건은 각 세포 유형에 따라 다르지만 일반적으로 필수 영양소(아미노산, 탄수화물, 비타민, 무기질), 성장인자, 호르몬, 가스(이산화탄소, 산소)를 공급하는 기질 또는 배지가 있는 적합한 용기로 구성된다. 이는 물리화학적 환경(완충 용액, 삼투압, 온도)을 조절할 수 있게 설계되었다. 대부분의 세포는 단층(하나의 단일 세포 두께)으로 부착 배양을 형성하기 위해 표면 또는 인공 기질이 필요한 반면, 어떤 세포는 현탁액 배양으로 배지에 자유롭게 떠서 성장할 수 있다.[1] 대부분의 세포의 수명은 유전적으로 결정되지만 일부 세포 배양 세포는 최적의 조건이 제공되면 무한정 재생되도록 변환되기도 한다.
실제로 세포 배양이라는 용어는 식물 조직 배양, 진균 배양, 미생물 배양의 뜻보다 동물 세포에서 유래된 세포의 배양을 의미한다. 세포 배양의 역사적 발전과 방법은 조직 배양 및 장기 배양 과 밀접한 관련이 있다. 바이러스의 숙주인 세포와 함께 바이러스 배양도 관련이 있다.[2][3]
포유류 세포 배양의 개념
세포의 분리
세포는 여러 가지 방법으로 생체 외 배양을 위해 조직에서 분리한다. 세포는 현탁액으로 방출하기 위해 조직을 교반하기 전에 콜라겐 분해 효소, 트립신, 프로네이스와 같은 효소를 사용하여 세포 외 기질을 소화함으로써 고체 조직에서 분리한다.[4][5] 또는 조직 조각을 배지에 넣고 세포를 배양할 수 있다.
피험자로부터 직접 배양 된 세포를 1차 세포라고 한다. 일부 종양에서 유래한 것을 제외하고 대부분의 1차 세포는 수명이 제한되어 있다.
불멸 세포주는 무작위 돌연변이 또는 텔로머레이스 유전자의 인공적인 발현과 같은 의도적인 변형을 통해 무기한 증식하는 능력을 획득하였다. 특정 세포 유형을 대표하는 수 많은 세포주가 존재한다.
배양을 통한 세포 유지
대부분의 분리된 1차 세포는 생물학적 노화 과정을 거치고 일반적인 생존 능력(Hayflick 한계)을 유지하면서 특정 인구 수가 되면 분열을 멈춘다.

온도 및 가스 혼합물을 제외하고 배양 시스템에서 가장 일반적인 변화 요소는 세포 성장 배지이다. 성장 배지의 제조법은 수소 이온 농도 지수, 포도당 농도, 성장 인자 및 기타 영양소의 존재의 여부에 따라 다르다. 배지를 보충하는 데 사용되는 성장 인자는 종종 소태아혈청(FBS), 송아지 혈청, 말혈청, 돼지 혈청과 같은 동물 혈액의 혈청에서 파생된다. 이러한 혈액 유래 성분 성장 인자의 단점은 특히 의료 생명공학기술 응용 분야에서 바이러스 또는 프리온으로 배양물이 오염될 가능성이 있다는 것이다. 현재는 이러한 성분의 사용을 최소화하거나 제거하고 인간 혈소판 용해물(hPL)를 사용함으로 그 단점을 줄일 수 있다.[6] 이것은 FBS를 인간 세포와 함께 사용할 때 종간 오염에 대한 걱정을 없애준다. hPL은 FBS 또는 기타 동물 혈청을 직접 대체하는 안전하고 신뢰할 수 있는 대안으로 부상했다. 또한, 화학 배지를 사용하여 혈청 흔적(인간 또는 동물)을 제거할 수 있지만 이는 다른 세포 유형에서 항상 달성할 수 있는 것은 아니다. 대체 전략에는 미국, 호주 및 뉴질랜드와 같이 BSE/TSE 위험이 최소인 국가에서 동물 혈액을 조달하고[7] 세포 배양을 위해 전 동물 혈청 대신 혈청에서 추출한 정제된 영양 농축액을 사용하는 것이 포함된다.[8]
Plating 밀도(배양 배지 부피 당 세포 수)는 일부 세포 유형에서 중요한 역할을 한다. 예를 들어, Plating 밀도가 낮을수록 과립막 세포는 에스트로겐 생성을 나타내지만 Plating 밀도가 높으면 프로게스테론을 생성하는 테카 루테인 세포로 나타난다.[9]
세포는 현탁액 또는 부착 배양으로 성장할 수 있다.[10] 일부 세포는 혈류에 존재하는 세포와 같이 표면에 부착되지 않고 자연적으로 부유 상태로 존재한다. 부착 조건이 허용하는 것보다 더 높은 밀도로 성장할 수 있도록 현탁액 배양에서 생존할 수 있도록 변형된 세포주도 있다. 부착 세포는 부착 특성을 증가시키고 성장 및 분화에 필요한 기타 신호를 제공하기 위해 세포외 기질(콜라겐 및 라미닌) 성분으로 코팅될 수 있는 조직 배양 플라스틱 또는 미세 담체와 같은 표면이 필요하다. 고형 조직에서 유래한 대부분의 세포는 부착되어 있다. 부착 배양의 또 다른 유형은 2차원 배양 접시와 달리 3차원 환경에서 세포를 성장시키는 것을 포함하는 Organotypic 배양이다. 이 3D 배양 시스템은 생화학적 및 생리학적으로 생체 내 조직과 더 유사하지만 많은 요인(확산 등)으로 인해 유지 관리하기가 기술적으로 어렵다.[11]
세포 배양 기초 배지
생명과학에서 일상적으로 사용되는 세포 배양 배지이다.
- MEM
- DMEM
- RPMI 1640
- Ham's F-12
- IMDM
- Leibovitz L-15
- DMEM/F-12
세포 배양 배지의 구성 요소
| 요소 | 기능 |
|---|---|
| 탄소원(포도당/글루타민) | 에너지원 |
| 아미노산 | 단백질 제공 |
| 비타민 | 세포 생존 및 성장 촉진 |
| 적절한 농도의 염 | 세포 내에서 최적의 삼투압을 유지하고 효소 반응, 세포 부착 등의 보조 인자로 작용하는 필수 금속 이온을 제공하기 위한 이온의 등장성 혼합물 |
| 페놀 레드 염료 | 산·염기 지시약. 페놀 레드의 색상은 pH 7~7.4에서 주황색(혹은 빨간색)에서 산성에서는 노란색으로, 염기성에서는 자주색으로 바뀐다. |
| 중탄산염/HEPES 완충 용액 | 배지에서 균형 잡힌 수소 이온 농도를 유지하는 데 사용된다. |
전형적인 성장 조건
| 조건 | |
|---|---|
| 온도 | 37°C |
| 이산화탄소 | 5% |
| 상대 습도 | 95% |
세포주 교차 오염
세포주 교차 오염은 배양된 세포를 다루는 과학자에게 문제가 될 수 있다.[12] 연구에 따르면 15~20%의 시간에서 실험에 사용된 세포가 잘못 식별되었거나 다른 세포주로 오염된 것으로 나타났다.[13][14][15] 세포주 교차 오염 문제는 약물 스크리닝 연구에 일상적으로 사용되는 NCI-60의 세포주에서도 감지되었다.[16][17] ATCC(American Type Culture Collection), ECACC(European Collection of Cell Cultures), DSMZ(German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures)를 포함한 주요 세포주 저장소는 연구자로부터 잘못 식별된 세포주 제출을 받았다.[16][18] 이러한 오염은 세포 배양주를 사용하여 생산된 연구의 품질에 문제를 제기할 수 있다.[19] ATCC는 짧은 탠덤 반복( Short Tandem Repeat, STR), DNA 지문을 사용하여 오염되지 않은 세포주로 인증한다.[20]
세포주 교차 오염 문제를 해결하기 위해 연구자들은 세포주의 정체성을 확립하기 위해 초기 계대에서 세포주를 인증하는 것이 좋다. 세포주를 동결하기 전, 활성 배양 동안 2개월마다, 그리고 세포주를 사용하여 생성된 연구 데이터를 출판하기 전에 인증을 반복해야 한다. 동질효소 분석, 인간 림프구 항원(HLA) 유형, 염색체 분석, 핵형 분석, 형태학 및 STR 분석을 비롯한 많은 방법이 세포주를 식별하는 데 사용된다.[20]
중요한 세포주 교차 오염의 예중 하나는 헬라 세포주이다.
기타 기술적 문제
세포는 일반적으로 배양에서 계속 분열하기 때문에 일반적으로 사용 가능한 영역 또는 부피를 채우기 위해 성장한다. 이로 인해 몇 가지 문제가 발생할 수 있다.
- 성장 배지의 영양 고갈
- 성장 배지의 pH 변화
- 세포 자살/괴사 세포의 축적
- 세포 간 접촉은 세포 주기 정지를 자극하여 세포가 분열을 멈추게 하는 접촉 억제
- 세포 간 접촉에 따른 세포 분화
- 유전적 및 후성적 변화, 변형된 세포의 자연 선택으로 잠재적으로 분화가 감소하고 증식 능력이 증가된 비정상적 배양 적응 세포의 과성장[21]
배지의 선택은 영양 성분과 농도의 차이로 인해 세포 배양 실험 결과의 생리학적 관련성에 영향을 미칠 수 있다.[22][23] 영양소의 생리학적 수준을 더 잘 나타내는 배지를 사용하면 생체 외 연구의 생리적 관련성을 향상 시킬 수 있으며 최근에는 Plasmax[24] 및 Human Plasma Like Medium(HPLM)[25] 과 같은 배지 유형이 개발되었다.
배양 세포의 조작
배양 세포에서 수행되는 일반적인 조작 중에는 배지 변경, 세포 계대, 세포 형질 주입이 있다. 이들은 일반적으로 무균 기술에 의존하는 조직 배양 방법을 사용하여 수행된다. 무균 기술은 세균, 효모 또는 기타 세포주의 오염을 방지하는 것을 목표로 한다. 조작은 일반적으로 오염 미생물을 배제하기 위해 생물 안전 작업대 또는 층류 작업대에서 수행된다. 항생제(페니실린, 스트렙토마이신) 및 항진균제(암포테리신 B)도 배지에 첨가할 수 있다.
세포가 대사 과정을 거치면서 산이 생성되고 pH가 감소한다. 산·염기 지시약을 배지에 첨가하여 영양소 고갈을 측정한다.
부착 배양의 경우 흡인에 의해 배지를 직접 제거한 다음 교체할 수 있다.
세포의 Passage
계대 배양에는 소수의 세포를 새 용기로 옮기는 작업이 포함된다. 세포를 규칙적으로 분할하면 장기간 높은 세포 밀도와 관련된 노화를 방지하므로 세포를 더 오랜 시간 동안 배양할 수 있다. 현탁 배양은 더 많은 양의 신선한 배지에 희석된 몇 개의 세포를 포함하는 소량의 배양으로 쉽게 계대된다. 부착 배양의 경우 먼저 용기에서 세포를 분리해야 한다. 트립신/EDTA의 혼합물을 이용한다. 그런 다음 소수의 분리된 세포를 사용하여 새로운 용기에 옮겨 담는다. RAW 세포와 같은 일부 세포 배양은 고무 Scraper로 용기 표면에서 물리적으로 긁어낸다.
형질 전환 및 형질 도입
세포를 조작하는 또 다른 일반적인 방법은 형질 주입에 의한 외래 DNA의 도입을 포함한다. 이것은 세포가 관심 유전자를 발현하도록 하기 위해 수행된다. 최근에 RNA 간섭 구조의 형질 주입은 특정 유전자 및 단백질의 발현을 억제하기 위한 편리한 메커니즘으로 실현되었다. 또한 DNA는 형질 도입 또는 형질 전환이라고 하는 방법으로 바이러스를 사용하여 세포에 삽입될 수 있다. 바이러스는 기생체이기 때문에 정상적인 번식 과정의 일부이기 때문에 DNA를 세포에 도입하는 데 매우 적합하다.
확립된 인간 세포주
일반적인 세포주
- 인간 세포주
- DU145 (전립선암)
- H295R (부신피질암)
- HeLa ( 자궁경부암 )
- KBM-7 (만성 골수성 백혈병)
- LNCaP (전립선암)
- MCF-7 (유방암)
- MDA-MB-468 (유방암)
- PC3 (전립선암)
- SaOS-2 (골종양)
- SH-SY5Y (신경모세포종, 다발성 골수종)
- T-47D (유방암)
- THP-1 (급성 골수성 백혈병)
- U87 (교모세포종)
- 영장류 세포주
- 쥐 세포주
- MC3T3 (배아 Calvarium)
- 쥐 종양 세포주
- 식물 세포주
- 기타 종 세포주
| Cell line | Meaning | Organism | Origin tissue | Morphology | Links |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3T3-L1 | "3-day transfer, inoculum 3 x 10^5 cells" | Mouse | Embryo | Fibroblast | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| 4T1 | Mouse | Mammary gland | ATCC Cellosaurus | ||
| 1321N1 | Human | Brain | Astrocytoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| 9L | Rat | Brain | Glioblastoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| A172 | Human | Brain | Glioblastoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| A20 | Mouse | B lymphoma | B lymphocyte | Cellosaurus | |
| A253 | Human | Submandibular duct | Head and neck carcinoma | ATCC Cellosaurus | |
| A2780 | Human | Ovary | Ovarian carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| A2780ADR | Human | Ovary | Adriamycin-resistant derivative of A2780 | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| A2780cis | Human | Ovary | Cisplatin-resistant derivative of A2780 | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| A431 | Human | Skin epithelium | Squamous cell carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| A549 | Human | Lung | Lung carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| AB9 | Zebrafish | Fin | Fibroblast | ATCC Cellosaurus | |
| AHL-1 | Armenian Hamster Lung-1 | Hamster | Lung | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| ALC | Mouse | Bone marrow | Stroma | PMID 2435412[26] Cellosaurus | |
| B16 | Mouse | Melanoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | ||
| B35 | Rat | Neuroblastoma | ATCC Cellosaurus | ||
| BCP-1 | Human | PBMC | HIV+ primary effusion lymphoma | ATCC Cellosaurus | |
| BEAS-2B | Bronchial epithelium + Adenovirus 12-SV40 virus hybrid (Ad12SV40) | Human | Lung | Epithelial | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| bEnd.3 | Brain Endothelial 3 | Mouse | Brain/cerebral cortex | Endothelium | Cellosaurus |
| BHK-21 | Baby Hamster Kidney-21 | Hamster | Kidney | Fibroblast | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| BOSC23 | Packaging cell line derived from HEK 293 | Human | Kidney (embryonic) | Epithelium | Cellosaurus |
| BT-20 | Breast Tumor-20 | Human | Breast epithelium | Breast carcinoma | ATCC Cellosaurus |
| BxPC-3 | Biopsy xenograft of Pancreatic Carcinoma line 3 | Human | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Epithelial | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| C2C12 | Mouse | Myoblast | ECACC Cellosaurus | ||
| C3H-10T1/2 | Mouse | Embryonic mesenchymal cell line | ECACC Cellosaurus | ||
| C6 | Rat | Brain astrocyte | Glioma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| C6/36 | Insect - Asian tiger mosquito | Larval tissue | ECACC Cellosaurus | ||
| Caco-2 | Human | Colon | Colorectal carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| Cal-27 | Human | Tongue | Squamous cell carcinoma | ATCC Cellosaurus | |
| Calu-3 | Human | Lung | Adenocarcinoma | ATCC Cellosaurus | |
| CGR8 | Mouse | Embryonic stem cells | ECACC Cellosaurus | ||
| CHO | Chinese Hamster Ovary | Hamster | Ovary | Epithelium | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| CML T1 | Chronic myeloid leukemia T lymphocyte 1 | Human | CML acute phase | T cell leukemia | DSMZ Cellosaurus |
| CMT12 | Canine Mammary Tumor 12 | Dog | Mammary gland | Epithelium | Cellosaurus |
| COR-L23 | Human | Lung | Lung carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| COR-L23/5010 | Human | Lung | Lung carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| COR-L23/CPR | Human | Lung | Lung carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| COR-L23/R23- | Human | Lung | Lung carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| COS-7 | Cercopithecus aethiops, origin-defective SV-40 | Old World monkey - Cercopithecus aethiops (Chlorocebus) | Kidney | Fibroblast | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| COV-434 | Human | Ovary | Ovarian granulosa cell carcinoma | PMID 8436435[27] ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| CT26 | Mouse | Colon | Colorectal carcinoma | Cellosaurus | |
| D17 | Dog | Lung metastasis | Osteosarcoma | ATCC Cellosaurus | |
| DAOY | Human | Brain | Medulloblastoma | ATCC Cellosaurus | |
| DH82 | Dog | Histiocytosis | Monocyte/macrophage | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| DU145 | Human | Androgen insensitive prostate carcinoma | ATCC Cellosaurus | ||
| DuCaP | Dura mater cancer of the Prostate | Human | Metastatic prostate carcinoma | Epithelial | PMID 11317521[28] Cellosaurus |
| E14Tg2a | Mouse | Embryonic stem cells | ECACC Cellosaurus | ||
| EL4 | Mouse | T cell leukemia | ECACC Cellosaurus | ||
| EM-2 | Human | CML blast crisis | Ph+ CML line | DSMZ Cellosaurus | |
| EM-3 | Human | CML blast crisis | Ph+ CML line | DSMZ Cellosaurus | |
| EMT6/AR1 | Mouse | Mammary gland | Epithelial-like | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| EMT6/AR10.0 | Mouse | Mammary gland | Epithelial-like | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| FM3 | Human | Lymph node metastasis | Melanoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| GL261 | Glioma 261 | Mouse | Brain | Glioma | Cellosaurus |
| H1299 | Human | Lung | Lung carcinoma | ATCC Cellosaurus | |
| HaCaT | Human | Skin | Keratinocyte | CLS Cellosaurus | |
| HCA2 | Human | Colon | Adenocarcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| HEK 293 | Human Embryonic Kidney 293 | Human | Kidney (embryonic) | Epithelium | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| HEK 293T | HEK 293 derivative | Human | Kidney (embryonic) | Epithelium | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| HeLa | "Henrietta Lacks" | Human | Cervix epithelium | Cervical carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| Hepa1c1c7 | Clone 7 of clone 1 hepatoma line 1 | Mouse | Hepatoma | Epithelial | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| Hep G2 | Human | Liver | Hepatoblastoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| High Five | Insect (moth) - Trichoplusia ni | Ovary | Cellosaurus | ||
| HL-60 | Human Leukemia-60 | Human | Blood | Myeloblast | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| HT-1080 | Human | Fibrosarcoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | ||
| HT-29 | Human | Colon epithelium | Adenocarcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| J558L | Mouse | Myeloma | B lymphocyte cell | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| Jurkat | Human | White blood cells | T cell leukemia | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| JY | Human | Lymphoblastoid | EBV-transformed B cell | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| K562 | Human | Lymphoblastoid | CML blast crisis | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| KBM-7 | Human | Lymphoblastoid | CML blast crisis | Cellosaurus | |
| KCL-22 | Human | Lymphoblastoid | CML | DSMZ Cellosaurus | |
| KG1 | Human | Lymphoblastoid | AML | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| Ku812 | Human | Lymphoblastoid | Erythroleukemia | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| KYO-1 | Kyoto-1 | Human | Lymphoblastoid | CML | DSMZ Cellosaurus |
| L1210 | Mouse | Lymphocytic leukemia | Ascitic fluid | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| L243 | Mouse | Hybridoma | Secretes L243 mAb (against HLA-DR) | ATCC Cellosaurus | |
| LNCaP | Lymph Node Cancer of the Prostate | Human | Prostatic adenocarcinoma | Epithelial | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| MA-104 | Microbiological Associates-104 | African Green Monkey | Kidney | Epithelial | Cellosaurus |
| MA2.1 | Mouse | Hybridoma | Secretes MA2.1 mAb (against HLA-A2 and HLA-B17) | ATCC Cellosaurus | |
| Ma-Mel 1, 2, 3....48 | Human | Skin | A range of melanoma cell lines | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| MC-38 | Mouse Colon-38 | Mouse | Colon | Adenocarcinoma | Cellosaurus |
| MCF-7 | Michigan Cancer Foundation-7 | Human | Breast | Invasive breast ductal carcinoma ER+, PR+ | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| MCF-10A | Michigan Cancer Foundation-10A | Human | Breast epithelium | ATCC Cellosaurus | |
| MDA-MB-157 | M.D. Anderson - Metastatic Breast-157 | Human | Pleural effusion metastasis | Breast carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| MDA-MB-231 | M.D. Anderson - Metastatic Breast-231 | Human | Pleural effusion metastasis | Breast carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| MDA-MB-361 | M.D. Anderson - Metastatic Breast-361 | Human | Melanoma (contaminated by M14) | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| MDA-MB-468 | M.D. Anderson - Metastatic Breast-468 | Human | Pleural effusion metastasis | Breast carcinoma | ATCC Cellosaurus |
| MDCK II | Madin Darby Canine Kidney II | Dog | Kidney | Epithelium | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| MG63 | Human | Bone | Osteosarcoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| MIA PaCa-2 | Human | Prostate | Pancreatic Carcinoma | ATCC Cellosaurus | |
| MOR/0.2R | Human | Lung | Lung carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| Mono-Mac-6 | Human | White blood cells | Myeloid metaplasic AML | DSMZ Cellosaurus | |
| MRC-5 | Medical Research Council cell strain 5 | Human | Lung (fetal) | Fibroblast | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| MTD-1A | Mouse | Epithelium | Cellosaurus | ||
| MyEnd | Myocardial Endothelial | Mouse | Endothelium | Cellosaurus | |
| NCI-H69 | Human | Lung | Lung carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| NCI-H69/CPR | Human | Lung | Lung carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| NCI-H69/LX10 | Human | Lung | Lung carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| NCI-H69/LX20 | Human | Lung | Lung carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| NCI-H69/LX4 | Human | Lung | Lung carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| Neuro-2a | Mouse | Nerve/neuroblastoma | Neuronal stem cells | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| NIH-3T3 | NIH, 3-day transfer, inoculum 3 x 105 cells | Mouse | Embryo | Fibroblast | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| NALM-1 | Human | Peripheral blood | Blast-crisis CML | ATCC Cellosaurus | |
| NK-92 | Human | Leukemia/lymphoma | ATCC Cellosaurus | ||
| NTERA-2 | Human | Lung metastasis | Embryonal carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| NW-145 | Human | Skin | Melanoma | ESTDAB Cellosaurus | |
| OK | Opossum Kidney | Virginia opossum - Didelphis virginiana | Kidney | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| OPCN / OPCT cell lines | Human | Prostate | Range of prostate tumour lines | Cellosaurus | |
| P3X63Ag8 | Mouse | Myeloma | ECACC Cellosaurus | ||
| PANC-1 | Human | Duct | Epithelioid Carcinoma | ATCC Cellosaurus | |
| PC12 | Rat | Adrenal medulla | Pheochromocytoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| PC-3 | Prostate Cancer-3 | Human | Bone metastasis | Prostate carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| Peer | Human | T cell leukemia | DSMZ Cellosaurus | ||
| PNT1A | Human | Prostate | SV40-transformed tumour line | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| PNT2 | Human | Prostate | SV40-transformed tumour line | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| Pt K2 | The second cell line derived from Potorous tridactylis | Long-nosed potoroo - Potorous tridactylus | Kidney | Epithelial | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| Raji | Human | B lymphoma | Lymphoblast-like | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| RBL-1 | Rat Basophilic Leukemia-1 | Rat | Leukemia | Basophil cell | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| RenCa | Renal Carcinoma | Mouse | Kidney | Renal carcinoma | ATCC Cellosaurus |
| RIN-5F | Mouse | Pancreas | ECACC Cellosaurus | ||
| RMA-S | Mouse | T cell tumour | Cellosaurus | ||
| S2 | Schneider 2 | Insect - Drosophila melanogaster | Late stage (20–24 hours old) embryos | ATCC Cellosaurus | |
| SaOS-2 | Sarcoma OSteogenic-2 | Human | Bone | Osteosarcoma | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| Sf21 | Spodoptera frugiperda 21 | Insect (moth) - Spodoptera frugiperda | Ovary | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| Sf9 | Spodoptera frugiperda 9 | Insect (moth) - Spodoptera frugiperda | Ovary | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| SH-SY5Y | Human | Bone marrow metastasis | Neuroblastoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| SiHa | Human | Cervix epithelium | Cervical carcinoma | ATCC Cellosaurus | |
| SK-BR-3 | Sloan-Kettering Breast cancer 3 | Human | Breast | Breast carcinoma | DSMZ Cellosaurus |
| SK-OV-3 | Sloan-Kettering Ovarian cancer 3 | Human | Ovary | Ovarian carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| SK-N-SH | Human | Brain | Epithelial | ATCC Cellosaurus | |
| T2 | Human | T cell leukemia/B cell line hybridoma | ATCC Cellosaurus | ||
| T-47D | Human | Breast | Breast ductal carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| T84 | Human | Lung metastasis | Colorectal carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| T98G | Human | Glioblastoma-astrocytoma | Epithelium | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| THP-1 | Human | Monocyte | Acute monocytic leukemia | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| U2OS | Human | Osteosarcoma | Epithelial | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| U373 | Human | Glioblastoma-astrocytoma | Epithelium | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| U87 | Human | Glioblastoma-astrocytoma | Epithelial-like | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| U937 | Human | Leukemic monocytic lymphoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | ||
| VCaP | Vertebral Cancer of the Prostate | Human | Vertebra metastasis | Prostate carcinoma | ECACC Cellosaurus |
| Vero | From Esperanto: verda (green, for green monkey) reno (kidney) | African green monkey - Chlorocebus sabaeus | Kidney epithelium | ECACC Cellosaurus | |
| VG-1 | Human | Primary effusion lymphoma | Cellosaurus | ||
| WM39 | Human | Skin | Melanoma | ESTDAB Cellosaurus | |
| WT-49 | Human | Lymphoblastoid | ECACC Cellosaurus | ||
| YAC-1 | Mouse | Lymphoma | ECACC Cellosaurus | ||
| YAR | Human | Lymphoblastoid | EBV-transformed B cell | Human Immunology[29] ECACC Cellosaurus |
참고
- 생물학에서의 영생
- 세포 배양 분석
- 전기적 세포-기질 임피던스 감지
- 오염된 세포주 목록
- NCI-60 세포주의 목록
- 유방암 세포주 목록
- 미세생리계
- ↑ Harris, AR; Peter, L; Bellis, J; Baum, B; Kabla, AJ; Charras, GT (2012년 10월 9일). “Characterizing the mechanics of cultured cell monolayers.”. 《Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America》 109 (41): 16449–54. doi:10.1073/pnas.1213301109. PMC 3478631. PMID 22991459.
- ↑ “Some landmarks in the development of tissue and cell culture”. 2006년 4월 19일에 확인함.
- ↑ “Cell Culture”. 2006년 4월 19일에 확인함.
- ↑ “Methods for isolating atrial cells from large mammals and humans”. 《Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology》 86: 187–98. September 2015. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.07.006. PMID 26186893.
- ↑ “Methods in cardiomyocyte isolation, culture, and gene transfer”. 《Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology》 51 (3): 288–98. September 2011. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.06.012. PMC 3164875. PMID 21723873.
- ↑ Hemeda, H., Giebel, B., Wagner, W. (16Feb2014) Evaluation of human platelet lysate versus fetal bovine serum for culture of mesenchymal stromal cells Cytotherapy p170-180 issue 2 doi.10.1016
- ↑ “Post - Blog | Boval BioSolutions, LLC”. bovalco.com. 2014년 12월 2일에 확인함.
- ↑ “LipiMAX purified lipoprotein solution from bovine serum”. 《Selborne Biological Services》. 2006. 2012년 6월 8일에 원본 문서에서 보존된 문서. 2010년 2월 2일에 확인함.
- ↑ “Cell plating density alters the ratio of estrogenic to progestagenic enzyme gene expression in cultured granulosa cells”. 《Fertility and Sterility》 93 (6): 2050–5. April 2010. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.01.151. PMID 19324349.
- ↑ Jaccard, N; Macown, RJ; Super, A; Griffin, LD; Veraitch, FS; Szita, N (October 2014). “Automated and online characterization of adherent cell culture growth in a microfabricated bioreactor.”. 《Journal of Laboratory Automation》 19 (5): 437–43. doi:10.1177/2211068214529288. PMC 4230958. PMID 24692228.
- ↑ “Organotypic brain slice cultures: A review”. 《Neuroscience》 305: 86–98. October 2015. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.07.086. PMC 4699268. PMID 26254240.
- ↑ “Line of attack”. 《Science》 347 (6225): 938–40. February 2015. Bibcode:2015Sci...347..938N. doi:10.1126/science.347.6225.938. PMID 25722392.
- ↑ “False human hematopoietic cell lines: cross-contaminations and misinterpretations”. 《Leukemia》 13 (10): 1601–7. October 1999. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2401510. PMID 10516762.
- ↑ “Cross-contamination: HS-Sultan is not a myeloma but a Burkitt lymphoma cell line”. 《Blood》 98 (12): 3495–6. December 2001. doi:10.1182/blood.V98.12.3495. PMID 11732505.
- ↑ “Identity tests: determination of cell line cross-contamination”. 《Cytotechnology》 51 (2): 45–50. June 2006. doi:10.1007/s10616-006-9013-8. PMC 3449683. PMID 19002894.
- ↑ 가 나 “Cell biology. Cases of mistaken identity”. 《Science》 315 (5814): 928–31. February 2007. doi:10.1126/science.315.5814.928. PMID 17303729.
- ↑ “A case study in misidentification of cancer cell lines: MCF-7/AdrR cells (re-designated NCI/ADR-RES) are derived from OVCAR-8 human ovarian carcinoma cells”. 《Cancer Letters》 245 (1–2): 350–2. January 2007. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2006.01.013. PMID 16504380.
- ↑ “Widespread intraspecies cross-contamination of human tumor cell lines arising at source”. 《International Journal of Cancer》 83 (4): 555–63. November 1999. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19991112)83:4<555::AID-IJC19>3.0.CO;2-2. PMID 10508494.
- ↑ “HeLa cells 50 years on: the good, the bad and the ugly”. 《Nature Reviews. Cancer》 2 (4): 315–9. April 2002. doi:10.1038/nrc775. PMID 12001993.
- ↑ 가 나 Dunham, J.H.; Guthmiller, P. (2008). “Doing good science: Authenticating cell line identity” (PDF). 《Cell Notes》 22: 15–17. 2008년 10월 28일에 원본 문서 (PDF)에서 보존된 문서. 2008년 10월 28일에 확인함.
- ↑ “Genetic and epigenetic instability in human pluripotent stem cells”. 《Human Reproduction Update》 19 (2): 187–205. 2012. doi:10.1093/humupd/dms048. PMID 23223511.
- ↑ Lagziel S, GottliebE, Shlomi T (2020). “Mind your media”. 《Nature Metabolism》 2 (12): 1369–1372. doi:10.1038/s42255-020-00299-y. PMID 33046912.
- ↑ Lagziel S, Lee WD, Shlomi T (2019). “Inferring cancer dependencies on metabolic genes from large-scale genetic screens.”
|url=값 확인 필요 (도움말). 《BMC Biol》 17 (1): 37. doi:10.1186/s12915-019-0654-4. PMC 6489231. PMID 31039782. - ↑ Vande Voorde J, Ackermann T, Pfetzer N, Sumpton D, Mackay G, Kalna G; 외. (2019). “Improving the metabolic fidelity of cancer models with a physiological cell culture medium.”
|url=값 확인 필요 (도움말). 《Sci Adv》 5 (1): eaau7314. Bibcode:2019SciA....5.7314V. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aau7314. PMC 6314821. PMID 30613774. - ↑ Cantor JR, Abu-Remaileh M, Kanarek N, Freinkman E, Gao X, Louissaint A; 외. (2017). “Physiologic Medium Rewires Cellular Metabolism and Reveals Uric Acid as an Endogenous Inhibitor of UMP Synthase.”
|url=값 확인 필요 (도움말). 《Cell》 169 (2): 258–272.e17. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.03.023. PMC 5421364. PMID 28388410. - ↑ “A single bone marrow-derived stromal cell type supports the in vitro growth of early lymphoid and myeloid cells”. 《Cell》 48 (6): 997–1007. March 1987. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(87)90708-2. PMID 2435412.
- ↑ “Establishment and characterization of 7 ovarian carcinoma cell lines and one granulosa tumor cell line: growth features and cytogenetics”. 《International Journal of Cancer》 53 (4): 613–20. February 1993. doi:10.1002/ijc.2910530415. PMID 8436435.
- ↑ “Establishment and characterization of a new human prostatic cancer cell line: DuCaP”. 《In Vivo》 15 (2): 157–62. 2001. PMID 11317521.
- ↑ “Promiscuous T-cell recognition of a rubella capsid protein epitope restricted by DRB1*0403 and DRB1*0901 molecules sharing an HLA DR supertype”. 《Human Immunology》 59 (3): 149–57. March 1998. doi:10.1016/S0198-8859(98)00006-8. PMID 9548074.
