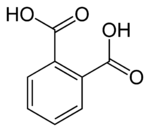
프탈산
| |
| |
| 이름 | |
|---|---|
| 우선명 (PIN)
benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid | |
| 별칭
1,2-benzenedioic acid,
phthalic acid, benzene-1,2-dioic acid, ortho-phthalic acid | |
| 식별자 | |
3D 모델 (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.703 |
| EC 번호 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| 성질 | |
| C8H6O4 | |
| 몰 질량 | 166.132 g/mol |
| 겉보기 | 흰색 고체 |
| 밀도 | 1.593 g/cm3, 고체 |
| 녹는점 | 207 °C (405 °F; 480 K)[3] |
| 0.6 g / 100 mL[1] | |
| 산성도 (pKa) | 2.89, 5.51[2] |
자화율 (χ)
|
-83.61·10−6 cm3/mol |
| 위험 | |
| NFPA 704 (파이어 다이아몬드) | |
| 관련 화합물 | |
관련 카복실산
|
아이소프탈산, 테레프탈산 |
관련 화합물
|
프탈산 무수물, 프탈이미드, 프탈하이드라자이드, 염화 프탈로일, 프탈알데하이드 |
달리 명시된 경우를 제외하면, 표준상태(25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa)에서 물질의 정보가 제공됨.
| |
프탈산(영어: phthalic acid) 또는 1,2-벤젠다이카복실산(영어: 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid)은 화학식이 C6H4(CO2H)2.인 방향족 다이카복실산이다. 프탈산은 상업적으로 중요하지는 않지만, 밀접하게 관련된 유도체인 프탈산 무수물은 대규모로 생산되는 필수 화학 물질이다.[4] 프탈산은 벤젠다이카복실산의 3가지 이성질체들 중 하나이며, 나머지는 아이소프탈산과 테레프탈산이다.
생산[편집]
프탈산은 나프탈렌 또는 오르토-자일렌을 프탈산 무수물로 직접 촉매 산화시킨 후 무수물을 가수분해하여 생성한다.[4]
프탈산은 1836년에 프랑스의 화학자인 오귀스트 로랑이 사염화 나프탈렌을 산화시켜 처음으로 생성하였다.[5] 그는 생성된 물질이 나프탈렌 유도체라고 믿었고, 생성물을 "나프탈산(naphthalic acid)"이라고 명명했다.[5][6] 이후에 스위스의 화학자인 장 샤를 갈리사르 드 마리냐크가 정확한 화학식을 결정한 후[7] 로랑이 현재의 이름을 부여했다.[5][8] 19세기의 제조 방법으로는 질산을 사용한 사염화 나프탈렌의 산화 또는 촉매로 수은 또는 황산 수은(II)를 사용하여 탄화수소를 발연 황산으로 산화시키는 것이 있다.[5]
합성[편집]
나프탈렌이 과망가니즈산 칼륨 또는 중크로뮴산 칼륨으로 산화되면 프탈산이 생성된다.
반응 및 용도[편집]
 |
프탈산은 pKa가 2.89와 5.51인 이염기산이다. 모노칼륨 염인 프탈산수소 칼륨은 분석화학의 표준산이다. 일반적으로 프탈산 에스터는 널리 이용가능한 프탈산 무수물로부터 제조된다. 물이 있는 상태에서 나트륨 아말감으로 프탈산을 환원시키면 1,3-사이클로헥사다이엔 유도체가 생성된다.[9]
안전[편집]
프탈산의 독성은 550 mg/kg의 LD50(쥐)로 보통이다.
생분해[편집]
세균인 Pseudomonas sp. P1은 프탈산을 분해한다.[10]
같이 보기[편집]
각주[편집]
- ↑ “PHTHALIC ACID”. 《hazard.com》.
- ↑ Brown, H.C., et al., in Baude, E.A. and Nachod, F.C., Determination of Organic Structures by Physical Methods, Academic Press, New York, 1955.
- ↑ Several melting points are reported, for example: (i) 480. K (NIST website), (ii) 210−211 °C with decomposition (Sigma-Aldrich on-line), (iii) 191 °C in a sealed tube (Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry), (iv) 230 °C with conversion to phthalic anhydride and water (J.T.Baker MSDS).
- ↑ 가 나 Lorz, Peter M.; Towae, Friedrich K.; Enke, Walter; Jäckh, Rudolf; Bhargava, Naresh; Hillesheim, Wolfgang (2007), 〈Phthalic Acid and Derivatives〉, 《울만 공업화학 백과사전(Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry)》, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, doi:10.1002/14356007.a20_181.pub2
- ↑ 가 나 다 라
 Chisholm, Hugh, 편집. (1911). 〈Phthalic Acids〉. 《브리태니커 백과사전》 21 11판. 케임브리지 대학교 출판부. 545–546쪽.
Chisholm, Hugh, 편집. (1911). 〈Phthalic Acids〉. 《브리태니커 백과사전》 21 11판. 케임브리지 대학교 출판부. 545–546쪽.
- ↑ See:
- Auguste Laurent (1836) "Sur l'acide naphtalique et ses combinaisons" (On naphthalic acid and its compounds), Annales de Chimie et de Physique, 61 : 113-125. (Note: The empirical formulae of the compounds that were analyzed in this article are incorrect, in part because, during this period, chemists used incorrect atomic masses for carbon (6 instead of 12) and other elements.)
- Reprinted in German as: Auguste Laurent (1836) "Ueber Naphthalinsäure und ihre Verbindungen" (On naphthalenic acid and its compounds), Annalen der Pharmacie, 19 (1) : 38-50; for the preparation of phthalic acid, see page 41.
- ↑ C. de Marignac (1841) "Ueber die Naphtalinsäure und ein bei ihrer Darstellung entstehendes flüchtiges Produkt" ("On naphthalinic acid and a volatile product that arises during its preparation"), Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie, 38 (1) : 13-20. (Note: Again, Marignac's empirical formulae are wrong because chemists at this time used incorrect atomic masses.)
- ↑ See:
- Auguste Laurent (1841) "Sur de nouvelles combinaisons nitrogénées de la naphtaline et sur les acides phtalique et nitrophtalique" (On new nitrogenous compounds of naphthalene, and on phthalic acid and nitrophthalic acid), Revue Scientifique et Industrielle, 6 : 76-99; on page 92, Laurent coins the name "acide phtalique" (phthalic acid) and admits that his earlier empirical formula for phthalic acid was wrong.
- Reprinted in German as: Auguste Laurent (1842) "Ueber neue stickstoffhaltige Verbindungen des Naphtalins, über Phtalinsäure und Nitrophtalinsäure" (On new nitrogenous compounds of naphthalene, on phthalic acid and nitrophthalic acid), Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie, 41 (1) : 98-114; on page 108, Laurent coins the name "Phtalinsäure" (phthalic acid).
- ↑ Richard N. McDonald and Charles E. Reineke (1988). “trans-1,2-Dihydrophthalic Acid”. 《Organic Syntheses》.; 《Collective Volume》 6, 461쪽
- ↑ Ishtiaq Ali, Muhammad (2011). 《Microbial degradation of polyvinyl chloride plastics》 (PDF) (Ph.D.). Quaid-i-Azam University. 47쪽. 2013년 12월 24일에 원본 문서 (PDF)에서 보존된 문서. 2022년 4월 4일에 확인함.
- Merck Index, 9th ed, #7178

