폴리염화 바이페닐
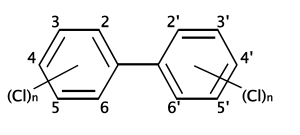
 PCB의 화학 구조.
| |
| 식별자 | |
|---|---|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.226 |
| UN 번호 | UN 2315 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| 성질 | |
| C12H10−xClx | |
| 몰 질량 | Variable |
| 겉보기 | Light yellow or colorless, thick, oily liquids[1] |
| 위험 | |
| NFPA 704 (파이어 다이아몬드) | |
달리 명시된 경우를 제외하면, 표준상태(25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa)에서 물질의 정보가 제공됨.
| |

폴리염화 바이페닐(영어: polychlorinated biphenyl, PCB)는 1에서 10개의 염소 원자들이 바이페닐에 붙어 있는 화학 물질을 일컫는다. 모든 PCB의 화학식은 C12H10-xClx이다.
사용[편집]
한때 살충제, 소화제, 밀봉제, 접착제, 도료등에 함유되어 있었으며,[2] 불연성이고 열 및 전기 절연성이 뛰어나 변압기와 축전기의 냉각제나 단열재로 쓰였다. 그러나 1970년대에 이들의 독성이 발견되면서 전 세계적으로 사용이 금지되었다. 생물에 축적되는 독극물 가운데 하나이다.
미국과 영국에서 "아스카렐(Askarel)"이라는 상표로 불렸다.
참조[편집]
- ↑ “Hazardous Substance Fact Sheet” (PDF). New Jersey Department of Health.
- ↑ Rudel, R A, Seryak, L M, and Brody, J G (2008). “PCB-containing wood floor finish is a likely source of elevated PCBs in resident's blood, household air and dust: a case study of exposure”. 《Environmental Health》: 2. doi:10.1186/1476-069X-7-2.
같이 보기[편집]
| 이 글은 화학에 관한 토막글입니다. 여러분의 지식으로 알차게 문서를 완성해 갑시다. |

