바르비투르산
| |||
| 이름 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 우선명 (PIN)
1,3-Diazinane-2,4,6-trione | |||
별칭
| |||
| 식별자 | |||
3D 모델 (JSmol)
|
|||
| 3DMet | |||
| 120502 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.598 | ||
| EC 번호 |
| ||
| 101571 | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| 성질 | |||
| C4H4N2O3 | |||
| 몰 질량 | 128.087 g·mol−1 | ||
| 겉보기 | White crystals | ||
| 녹는점 | 245 °C (473 °F; 518 K) | ||
| 끓는점 | 260 °C (500 °F; 533 K) | ||
| 142 g/l (20 °C) | |||
| 산성도 (pKa) | 4.01 (H2O)[1] | ||
자화율 (χ)
|
| ||
| 위험 | |||
| 물질 안전 보건 자료 | External MSDS | ||
| GHS 그림문자 | 
| ||
| 신호어 | 경고 | ||
| H315, H319, H335 | |||
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (파이어 다이아몬드) | |||
달리 명시된 경우를 제외하면, 표준상태(25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa)에서 물질의 정보가 제공됨.
| |||
바르비투르산(Barbituric acid)은 피리미딘 헤테로고리 스켈레톤 기반의 유기 화합물이다. 수용성 무색 가루이다. 바르비투르산은 바르비투르산계 약물의 부모 화합물이지만 바르비투르산 그 자체는 약물학적 반응을 보이지 않는다. 이 화합물은 아돌프 폰 바이어가 처음 합성하였다.
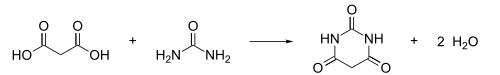
합성[편집]
건강과 안전[편집]
바르비투르산을 과복용하면 호흡 억제와 사망을 일으킬 수 있다.[2][3][4][5]
각주[편집]
- ↑ Haynes, William M., 편집. (2016). 《CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics》 97판. CRC Press. 5–89쪽. ISBN 978-1498754286.
- ↑ Boyd E M, Pearl M. Can nalorphine hydrochloride prevent respiratory depression and death from overdose of barbiturates?[J]. Canadian Medical Association Journal, 1955, 73(1):35-8.
- ↑ Koppanyi T, Fazekas J F. Acute Barbiturate Poisoning Analysis and Evaluation of Current Therapy[J]. American Journal of the Medical Sciences, 1950, 220(5):559-576.
- ↑ Shulman A, Shaw F H, Cass N M, et al. A New Treatment of Barbiturate Intoxication[J]. British Medical Journal, 1955, 1(4924):1238-44.
- ↑ Bateman C H. Barbiturate Poisoning[J]. Lancet, 1963, 282(7303):357.
외부 링크[편집]
- Mahmudov, K.T.; Kopylovich, M.N.; Maharramov, A.M.; Kurbanova, M.M.; Gurbanov, A.V.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. (2014). “Barbituric acids as a useful tool for the construction of coordination and supramolecular compounds”. 《Coordination Chemistry Reviews》 265: 1–37. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2014.01.002.



