게피오넬라속
|
| ||
|---|---|---|
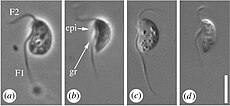 Gefionella okellyi의 광학현미경 사진 | ||
| 생물 분류ℹ️ | ||
| 역: | 진핵생물 | |
| 계: | 엑스카바타계 또는 말라이모나스계 | |
| 문: | 로우코조아문 또는 말라이모나스문 | |
| 강: | 말라이모나스강 | |
| 목: | 말라이모나스목 | |
| 과: | 말라이모나스과 | |
| 속: | 게피오넬라속 (Gefionella) Heiss, Ekelund & Simpson 2018[1] | |
| 모식종 | ||
| Gefionella okellyi | ||
| Heiss, Ekelund & Simpson 2018 | ||
| 종 | ||
| ||
게피오넬라속(Gefionella)은 진핵생물 진화의 기본 그룹인 말라이모나스과에 속하는 엑스카바타 원생생물 속이다.[2] 2018년에 기술된 Gefionella okellyi 종만 있는 단일 속이다. 게피오넬라속은 북유럽 여신 게푠(Gefjon)의 이름을 따서 명명되었으며, 종은 엑스카바타 편모에 대한 미세구조 및 계통발생학 연수의 선구자인 과학자 Charles J. O'Kelly의 이름을 따서 명명되었다.[1]
계통 분류[편집]
다음은 말라이모나스류의 계통 분류이다.[3]
| 말라이모나스류 |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
각주[편집]
- ↑ 가 나 Heiss AA, KoliskoM, Ekelund F, Brown MW, Roger AJ, Simpson AGB (2018). “Combined morphological and phylogenomic re-examination of malawimonads, a critical taxon for inferring the evolutionary history of eukaryotes”. 《R. Soc. Open Sci.》 5 (171707): 171707. doi:10.1098/rsos.171707. PMC 5936906. PMID 29765641. S2CID 21689695.
- ↑ Adl SM, Bass D, Lane CE, Lukeš J, Schoch CL, Smirnov A, Agatha S, Berney C, Brown MW, Burki F, Cárdenas P, Čepička I, Chistyakova L, del Campo J, Dunthorn M, Edvardsen B, Eglit Y, Guillou L, Hampl V, Heiss AA, Hoppenrath M, James TY, Karnkowska A, Karpov S, Kim E, Kolisko M, Kudryavtsev A, Lahr DJG, Lara E, Le Gall L, Lynn DH, Mann DG, Massana R, Mitchell EAD, Morrow C, Park JS, Pawlowski JW, Powell MJ, Richter DJ, Rueckert S, Shadwick L, Shimano S, Spiegel FW, Torruella G, Youssef N, Zlatogursky V, Zhang Q (2019). “Revisions to the Classification, Nomenclature, and Diversity of Eukaryotes”. 《Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology》 66 (1): 4–119. doi:10.1111/jeu.12691. PMC 6492006. PMID 30257078.
- ↑ Heiss AA, Warring SD, Lukacs K, Favate J, Yang A, Gyaltshen Y, Filardi C, Simpson AGB, Kim E (December 2020). “Description of Imasa heleensis, gen. nov., sp. nov. (Imasidae, fam. nov.), a Deep-Branching Marine Malawimonad and Possible Key Taxon in Understanding Early Eukaryotic Evolution”. 《Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology》 68: e12837. doi:10.1111/jeu.12837.
