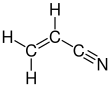
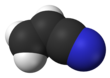
아크릴로나이트릴
보이기
| |||
| |||
| 이름 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 우선명 (PIN)
Prop-2-enenitrile | |||
| 별칭 | |||
| 식별자 | |||
3D 모델 (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.152 | ||
| EC 번호 |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS 번호 |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN 번호 | 1093 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| 성질 | |||
| C3H3N | |||
| 몰 질량 | 53.064 g·mol−1 | ||
| 겉보기 | Colourless liquid | ||
| 밀도 | 0.81 g/cm3 | ||
| 녹는점 | −84 °C (−119 °F; 189 K) | ||
| 끓는점 | 77 °C (171 °F; 350 K) | ||
| 70 g/L | |||
| log P | 0.19[2] | ||
| 증기 압력 | 83 mmHg[1] | ||
| 위험 | |||
| 주요 위험 | flammable reactive toxic potential occupational carcinogen[1] | ||
| 물질 안전 보건 자료 | ICSC 0092 | ||
| NFPA 704 (파이어 다이아몬드) | |||
| 인화점 | −1 °C; 30 °F; 272 K | ||
| 471 °C (880 °F; 744 K) | |||
| 폭발 한계 | 3–17% | ||
| 반수 치사량 또는 반수 치사농도 (LD, LC): | |||
LC50 (median concentration)
|
500 ppm (rat, 4 h) 313 ppm (mouse, 4 h) 425 ppm (rat, 4 h)[3] | ||
LCLo (lowest published)
|
260 ppm (rabbit, 4 h) 575 ppm (guinea pig, 4 h) 636 ppm (rat, 4 h) 452 ppm (human, 1 h)[3] | ||
| NIOSH (미국 건강 노출 한계): | |||
PEL (허용)
|
TWA 2 ppm C 10 ppm [15-minute] [skin][1] | ||
REL (권장)
|
Ca TWA 1 ppm C 10 ppm [15-minute] [skin][1] | ||
IDLH (직접적 위험)
|
85 ppm[1] | ||
| 관련 화합물 | |||
관련 nitriles
|
acetonitrile propionitrile | ||
관련 화합물
|
acrylic acid acrolein | ||
달리 명시된 경우를 제외하면, 표준상태(25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa)에서 물질의 정보가 제공됨.
| |||
아크릴로나이트릴(Acrylonitrile) 또는 아크릴로니트릴은 화학식 CH2CHCN을 갖는 유기 화합물이다. 무색의 휘발성 액체이지만 상업용 샘플은 불순성 때문에 노란색일 수 있다. 마늘향이나 양파향의 자극적인 냄새를 낸다.[4] 분자기하 면에서 나이트릴 하나에 연결된 바이닐기 하나로 구성된다. 폴리아크릴로나이트릴과 같은 유용한 플라스틱의 제조를 위한 중요한 단량체이다. 낮은 양에도 반응적이고 독성이 있다.[5] 1893년 프랑스의 화학자 Charles Moureu(1863-1929)가 처음 합성하였다.[6]
각주
[편집]- ↑ 가 나 다 라 마 바 사 아 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. “#0014”. 미국 국립 직업안전위생연구소 (NIOSH).
- ↑ “Acrylonitrile_msds”.
- ↑ 가 나 “Acrylonitrile”. 《Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH)》. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ “Medical Management Guidelines for Acrylonitrile”. Agency for Toxic Substances & Disease Registry. 2020년 6월 10일에 확인함.
- ↑ Brazdil, James F., 〈Acrylonitrile〉, 《울만 공업화학 백과사전(Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry)》, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, doi:10.1002/14356007.a01_177.pub3
- ↑
- Moureu, C. (1893). “Contribution à l'étude de l'acide acrylique et de ses dérivés” [Contribution to the study of acrylic acid and of its derivatives]. 《Annales de chimie et de physique》. 7th 2: 145–212. See especially pp. 187–189 ("Nitrile acrylique ou cyanure de vinyle (Propène-nitrile)").
- Moureu, C. (1893). “Nitrile acrylique, cyanure de vinyle (propène-nitrile)” [Acrylic nitrile, vinyl cyanide (propenenitrile)]. 《Bulletin de la Société Chimique de France》. 3rd 9: 424–427.
외부 링크
[편집]- National Pollutant Inventory – Acrylonitrile
- Comparing Possible Cancer Hazards from Human Exposures to Rodent Carcinogens Archived 2012년 9월 3일 - 웨이백 머신
- Acrylonitrile – Integrated Risk Information System, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
- CDC – NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards – Acrylonitrile
- OSHA Table Z-1 for Air Contaminants