2019년 5월 26일 (일) 22:10 판
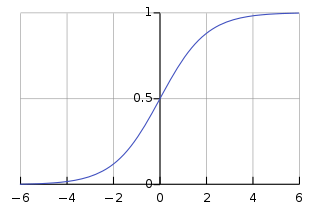
로지스틱 곡선 오류 함수 곡선시그모이드 함수 는 특성"S"형 곡선 또는 시그모이드 곡선을 갖는 수학 함수 입니다. 종종 시그 모이드 함수 는 첫 번째 그림에 표시된 로지스틱 함수 의 특수한 경우를 지칭하며 수식으로 정의됩니다
<mrow class="MJX-TeXAtom-ORD"><mstyle displaystyle="true" scriptlevel="0"><mi>
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
{\displaystyle }
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
S
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
=
e
x
e
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle S(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}}{e^{x}+1}}.}
정의 시그모이드 함수는 실함수로써 유계이며 미분가능한 함수이며, 모든 점에서의 미분값은 양수이다. [1]
성질 일반적으로 시그모이드함수는 단조함수 이며종 종 모양의 1차 미분 그래프를 가집니다. 시그모이드 함수는 </img>일 때, 한 쌍의 수평 점근선 으로 수렴한다.구문 분석 실패 (구문 오류): {\displaystyle <mrow class="MJX-TeXAtom-ORD"><mstyle displaystyle="true" scriptlevel="0"><mi> <math>x \rightarrow \pm \infty}
</mi><mo stretchy="false">
x
→
±
∞
{\displaystyle x\rightarrow \pm \infty }
x
→
±
∞
{\displaystyle x\rightarrow \pm \infty }
x
→
±
∞
{\displaystyle x\rightarrow \pm \infty }
x
→
±
∞
{\displaystyle x\rightarrow \pm \infty }
x
→
±
∞
{\displaystyle x\rightarrow \pm \infty }
시그모이드 함수는 0보다 작은 값에서 볼록하고 0보다 큰 값에서 오목하다.
예시 일부 시그모이드 함수에 대한 비교. 그림에서 모든 함수는 원점에서의 기울기가 1이되도록 정규화를 함. 구문 분석 실패 (구문 오류): {\displaystyle <mrow class="MJX-TeXAtom-ORD"><mstyle displaystyle="true" scriptlevel="0"><mi> <math> f(x) = \frac{1}{1 + e^{-x}} }
</mi><mo stretchy="false">
f
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
1
1
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {1}{1+e^{-x}}}}
구문 분석 실패 (구문 오류): {\displaystyle <mrow class="MJX-TeXAtom-ORD"><mstyle displaystyle="true" scriptlevel="0"><mi> <math> f(x) = \tanh x = \frac{e^x-e^{-x}}{e^x+e^{-x}} }
</mi><mo stretchy="false">
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
tanh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}}
구문 분석 실패 (구문 오류): {\displaystyle <mrow class="MJX-TeXAtom-ORD"><mstyle displaystyle="true" scriptlevel="0"><mi> <math> f(x) = \arctan x }
</mi><mo stretchy="false">
f
(
x
)
=
arctan
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\arctan x}
f
(
x
)
=
arctan
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\arctan x}
f
(
x
)
=
arctan
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\arctan x}
f
(
x
)
=
arctan
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\arctan x}
f
(
x
)
=
arctan
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\arctan x}
f
(
x
)
=
arctan
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\arctan x}
f
(
x
)
=
arctan
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\arctan x}
f
(
x
)
=
arctan
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\arctan x}
f
(
x
)
=
arctan
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\arctan x}
구문 분석 실패 (구문 오류): {\displaystyle <mrow class="MJX-TeXAtom-ORD"><mstyle displaystyle="true" scriptlevel="0"><mi> <math> f(x) = \operatorname{erf}(x) = \frac{2}{\sqrt{\pi}}\int_0^x e^{-t^2} \, dt }
</mi><mo stretchy="false">
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
f
(
x
)
=
erf
(
x
)
=
2
π
∫
0
x
e
−
t
2
d
t
{\displaystyle f(x)=\operatorname {erf} (x)={\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}\int _{0}^{x}e^{-t^{2}}\,dt}
구문 분석 실패 (구문 오류): {\displaystyle <mrow class="MJX-TeXAtom-ORD"><mstyle displaystyle="true" scriptlevel="0"><mi> <math> f(x) = \frac{x}{\sqrt{1+x^2}} }
</mi><mo stretchy="false">
f
(
x
)
=
x
1
+
x
2
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {x}{\sqrt {1+x^{2}}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
x
1
+
x
2
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {x}{\sqrt {1+x^{2}}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
x
1
+
x
2
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {x}{\sqrt {1+x^{2}}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
x
1
+
x
2
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {x}{\sqrt {1+x^{2}}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
x
1
+
x
2
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {x}{\sqrt {1+x^{2}}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
x
1
+
x
2
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {x}{\sqrt {1+x^{2}}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
x
1
+
x
2
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {x}{\sqrt {1+x^{2}}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
x
1
+
x
2
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {x}{\sqrt {1+x^{2}}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
x
1
+
x
2
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {x}{\sqrt {1+x^{2}}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
x
1
+
x
2
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {x}{\sqrt {1+x^{2}}}}}
f
(
x
)
=
x
1
+
x
2
{\displaystyle f(x)={\frac {x}{\sqrt {1+x^{2}}}}}
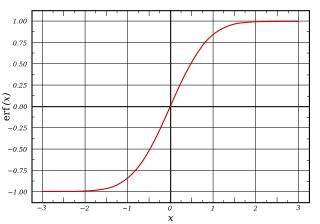
연속적이고 음이 아닌 "범프 모양"함수의 적분 은 S자형이므로, 많은 일반적인 확률 분포 에 대한 누적 분포 함수 역시 S자형 입니다. 한 가지 예가 정규 분포 의 누적 분포 함수와 관련된 오류 함수입니다.
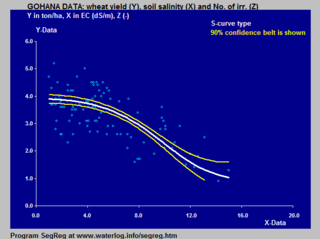
응용 밀 수확량과 토양 염분 사이의 관계를 모델링 한 역 시그모이드 곡선. [2] 복잡한 학습 곡선 과 같은 많은 자연적인 과정은 시간이 지남에 따라 낮은 시작점에서부터 최종단계까지 증가함따라 가속화하여 접근합니다. 특정 수학적 모델이 부족할 때, 시그모이드 함수가 자주 사용됩니다. [3]
인공 신경망 에서는 매끄럽지 않은 함수가 효율성 대신 사용됩니다. 이들은 hard Sigmoids 로 알려져 있습니다.
같이 보기 참고 문헌
↑ Han, Jun; Morag, Claudio (1995). 〈The influence of the sigmoid function parameters on the speed of backpropagation learning〉. Mira, José; Sandoval, Francisco. 《From Natural to Artificial Neural Computation》. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 930 . 195–201쪽. doi :10.1007/3-540-59497-3_175 . ISBN 978-3-540-59497-0 ↑ Software to fit an S-curve to a data set [1]
↑ Gibbs, M.N. (Nov 2000). “Variational Gaussian process classifiers”. 《IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks》 11 (6): 1458–1464. doi :10.1109/72.883477 . PMID 18249869 .
Mitchell, Tom M. (1997). 《Machine Learning》. WCB–McGraw–Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-042807-2 Humphrys, Mark. “Continuous output, the sigmoid function” .