CD14
CD14(세포표면항원무리 14)는 주로 대식세포에 의해 선천 면역 체계의 일부로 만들어지는 인간 단백질이다.[1][2] 병원체 연관 분자유형(PAMP)인 지질다당류(LPS)를 결합하여 체내 세균 검출에 도움을 준다.
CD14는 두 가지 형태로 존재하는데, 하나는 글리코실 포스파티딜 이노시톨(GPI) 꼬리(mCD14)에 의해 막에 고정되고, 다른 하나는 가용성 형태(sCD14)이다.[3]
CD14(4GLP.pdb)의 X선 결정 구조는 소수성 아미노 말단 포켓을 포함하는 단량체의 구부러진 솔레노이드 구조를 나타낸다.[4]
CD14는 최초로 기술된 유형인식수용체이다.
기능[편집]
CD14는 세균성 지질다당류(LPS)의 검출을 위한 공동 수용체(톨유사수용체 TLR4 및 MD-2) 역할을 한다.[5][6] CD14는 지질다당류 결합 단백질(LBP)이 있는 경우에만 LPS에 결합 할 수 있다. LPS는 주요 리간드로 간주되지만 CD14는 리포테이코산과 같은 다른 병원체 관련 분자 패턴도 인식한다.[7]
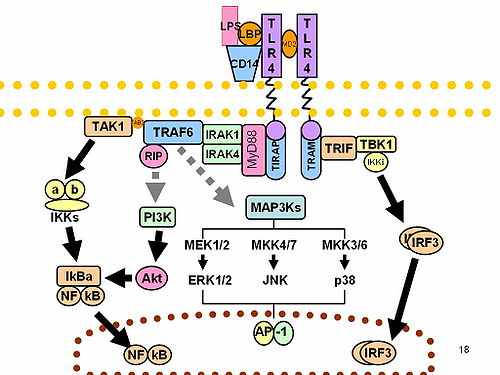
조직 분포[편집]
CD14는 주로 대식세포, 호중구에 의해 발현된다. 또한 수지상 세포에 의해 표현된다. 수용성 형태의 수용체(sCD14)는 간과 단핵구에 의해 분비되며 CD14를 발현하지 않는 세포에 LPS 반응성을 부여하기에 낮은 농도로 충분하다. mCD14 및 sCD14는 장 세포에 존재한다.[8] sCD14는 모유에도 존재하며, 유아의 장에서 미생물 성장을 조절하는 것으로 생각된다.
분화[편집]
CD14+ 단핵구는 과립구 대식세포 콜로니 자극 인자(GM-CSF) 및 인터루킨 4를 포함하여 사이토카인에 의해 촉진되는 분화경로 인 수지상 세포를 포함하여 다양한 세포로 분화 할 수 있다.
상호 작용[편집]
CD14는 지질다당류 결합 단백질과 상호 작용하는 것으로 나타났다.[9][10]
각주[편집]
- ↑ “Mouse and human CD14 (myeloid cell-specific leucine-rich glycoprotein) primary structure deduced from cDNA clones”. 《Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Gene Structure and Expression》 1008 (2): 213–22. July 1989. doi:10.1016/0167-4781(80)90012-3. PMID 2472171.
- ↑ “Monocyte antigen CD14 is a phospholipid anchored membrane protein”. 《Blood》 73 (1): 284–9. January 1989. doi:10.1182/blood.V73.1.284.284. PMID 2462937.
- ↑ “Structure-function analysis of soluble and membrane-bound CD14”. 《Progress in Clinical and Biological Research》 397: 79–87. 1998. PMID 9575549.
- ↑ “The crystal structure of human soluble CD14 reveals a bent solenoid with a hydrophobic amino-terminal pocket”. 《Journal of Immunology》 190 (3): 1304–11. February 2013. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1202446. PMC 3552104. PMID 23264655.
- ↑ “Role of CD14 in cellular recognition of bacterial lipopolysaccharides”. 《Chemical Immunology》. Chemical Immunology and Allergy 74: 61–82. 2000. doi:10.1159/000058750. ISBN 3-8055-6917-3. PMID 10608082.
- ↑ “Soluble CD14-mediated cellular responses to lipopolysaccharide”. 《Chemical Immunology》. Chemical Immunology and Allergy 74: 108–21. 2000. doi:10.1159/000058751. ISBN 3-8055-6917-3. PMID 10608084.
- ↑ “Human lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP) and CD14 independently deliver triacylated lipoproteins to Toll-like receptor 1 (TLR1) and TLR2 and enhance formation of the ternary signaling complex”. 《The Journal of Biological Chemistry》 288 (14): 9729–41. April 2013. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.453266. PMC 3617275. PMID 23430250.
- ↑ “CD14 Is Expressed and Released as Soluble CD14 by Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells In Vitro: Lipopolysaccharide Activation of Epithelial Cells Revisited”. 《Infection and Immunity》 69 (6): 3772–3781. June 2001. doi:10.1128/IAI.69.6.3772-3781.2001. PMC 98389. PMID 11349042.
- ↑ “Evidence of a trimolecular complex involving LPS, LPS binding protein and soluble CD14 as an effector of LPS response”. 《FEBS Letters》 531 (2): 184–8. November 2002. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03499-3. PMID 12417309.
- ↑ “LPS-dependent interaction of Mac-2-binding protein with immobilized CD14”. 《Journal of Inflammation》 45 (2): 115–25. 1995. PMID 7583357.
